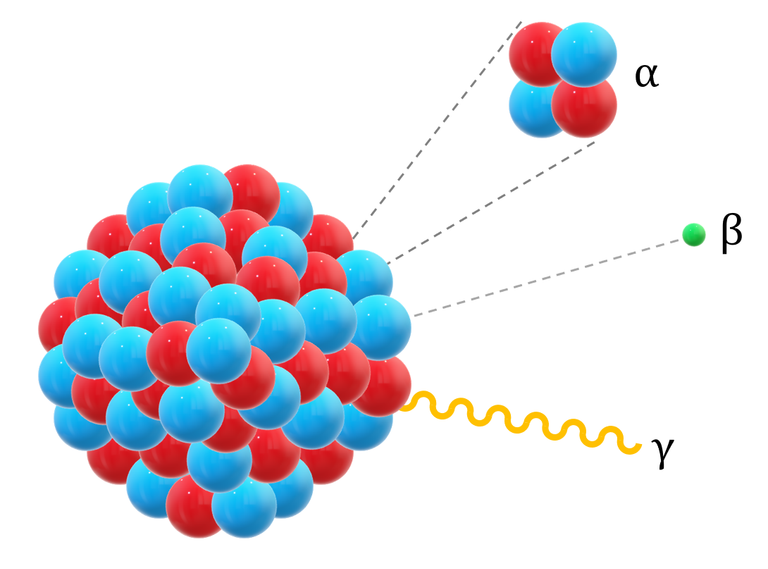
When the word Radioactivity is heard, what comes to mind is the emission of energy in form of radiation. Just like it is normal for you to breath, so is it appropriate for radioactive particle to emit radioactive energy so as to be able to neutralize and stabilize its nucleus and this is because this particles contain more neutron than proton and so will have to lose its neutron via emission until both neutron and proton ratio are equal then it becomes nonradioactive.
To understand radiation, we need to understand that radiation released by the nuclei of radioactive particles are of three types of emissions which are Alpha particles (atomic particle), Beta particles (subatomic particle), and Gamma radiation with their energy level increasing as mentioned. Alpha particles are weak radioactive emissions with two protons and two neutrons and to understand the extent of how weak its energy is, it cannot penetrate something as simple as a sheet of paper, so if you are putting on cloths, then you are protected from alpha particle emission although it doesn't really matter because it cannot penetrate the skin as well.
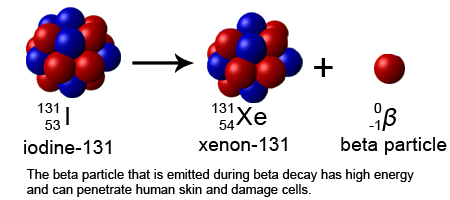
Beta particle have higher energy electrons compared to alpha particles and so their emission can penetrate through cloths and even woods and if you are exposed to it, they can cause skin burn as they can penetrate below the skin surface a little. Unless these radioactive particles are ingested or inhaled, they do not pose any threat when outside the body but when inside the body, they cause internal burns of tissues and organs which can lead to cancer.
commons.wikimedia.org
The third type of radiation is the gamma ray and this has more energy compared to the two we mentioned before. This high energy level accords them the name penetrating radiation and the name isn't far-fetched as it can pass through concrete, water, and certain metals. If this radiation can pass through these objects, then what is the body it cannot penetrate?
When this ray collides with an atom, it gets received by an electron which gets energized and displaced off its orbit and in the case of a bond, the same thing happens causing the bond to be broken and this is what causes damage in proteins and DNA in the body. When this ray hits cells, it fragments DNA, denatures protein, damage cell organelles, and destroys the cell at the end with cell repair not possible.
When a person is exposed to acute radiation poisoning, they can experience early symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea as a result of the GI tract cells being affected by the radiation. In a case where you do not know you are in a radioactive space, then it can lead to reduced red blood cell count as a result of the degeneration of the bone marrow in the body. With prolong exposure comes more damage to the body like the shutting down of the kidneys, lung, and the liver which will lead to death.
It is not like the person dies in few seconds or minutes. Actually, depending on the amount of radiation being exposed to, it can get to days, weeks, or months before these symptoms become manifest and death become inevitable and for all this to happen, it requires a high rate of emission from the source and a close proximity to the source. If you have read history books, then you must have read the story of Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombing from the United States. While the bomb had its effect, the gamma ray did more harm than the bomb itself. Another example is the Chernobyl Nuclear Power plant disaster that got people to suffer from Acute radiation exposure.
https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/focus/chernobyl/faqs
https://science.nasa.gov/ems/12_gammarays/
https://www.arpansa.gov.au/understanding-radiation/what-is-radiation/ionising-radiation/alpha-particles
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/alpha-radiation
https://www.epa.gov/radiation/radiation-basics
https://www.arpansa.gov.au/understanding-radiation/what-is-radiation/ionising-radiation/beta-particles
https://www.nrc.gov/about-nrc/radiation/health-effects/radiation-basics.html