▶️ Watch on 3Speak - Odysee - BitChute - Rumble - YouTube - PDF notes
In this video I go over the end-of-chapter True-False Quiz as a review for the Vectors and the Geometry of Space chapter. There are 22 questions in total covering vectors, cross products, dot products, lines, surfaces, and much more. This is a great review of the videos I had covered earlier and helps crystalize the topics covered.
Timestamps
- Intro: 0:00
- Calculus Book Reference: 0:58
- Sections in Calculus Book Chapter: 1:40
- Topics to Cover: 2:50
- True-False Quiz: 3:03
- Question 1: 3:17
- Question 2: 4:21
- Question 3: 7:56
- Question 4: 9:41
- Question 5: 12:10
- Question 6: 14:15
- Question 7: 15:58
- Question 8: 17:17
- Question 9: 21:02
- Question 10: 28:12
- Question 11: 33:25
- Question 12: 40:48
- Question 13: 50:19
- Question 14: 56:22
- Question 15: 59:16
- Question 16: 1:01:21
- Question 17: 1:01:55
- Question 18: 1:03:18
- Question 19: 1:05:57
- Question 20: 1:07:51
- Question 21: 1:09:26
- Question 22: 1:11:23
- Outro: 1:13:51
Video sections - Vectors and the Geometry of Space
View Video Notes Below!
Become a MES Super Fan - Donate - Subscribe via email - MES merchandise
Reuse of my videos:
- Feel free to make use of / re-upload / monetize my videos as long as you provide a link to the original video.
Fight back against censorship:
- Bookmark sites/channels/accounts and check periodically.
- Remember to always archive website pages in case they get deleted/changed.
Recommended Books: "Where Did the Towers Go?" by Dr. Judy Wood
Join my forums: Hive community - Reddit - Discord
Follow along my epic video series: MES Science - MES Experiments - Anti-Gravity (MES Duality) - Free Energy - PG
NOTE 1: If you don't have time to watch this whole video:
- Skip to the end for Summary and Conclusions (if available)
- Play this video at a faster speed.
-- TOP SECRET LIFE HACK: Your brain gets used to faster speed!
-- MES tutorial- Download and read video notes.
- Read notes on the Hive blockchain $HIVE
- Watch the video in parts.
-- Timestamps of all parts are in the description.Browser extension recommendations: Increase video speed - Increase video audio - Text to speech (Android app) – Archive webpages
Vectors and the Geometry of Space: True-False Quiz

Calculus Book Reference
Note that I mainly follow along the book:
- Calculus: Early Transcendentals 7th Edition by James Stewart
- Note: In some earlier videos I used the 6th edition.
For this video, I used this website for the Quiz solutions: Link
Sections in Calculus Book Chapter
I have made a list of the sections in this particular chapter with links to the Hive post of the videos I have already finished.
Note that I have started splitting each long video into sections and made a playlist for each.
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
- 3-D Coordinate Systems
- Vectors
- The Dot Product - Playlist
- The Cross Product - Playlist
- Equations of Lines and Planes - Playlist
- Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces - playlist
- Review - playlist
- Problems Plus - ▶️
This links are also on MES Links: https://mes.fm/links
Topics to Cover
Note that the timestamps will be included in the video description for each topic listed below.
- Question 1
- Question 2
- Question 3
- Question 4
- Question 5
- Question 6
- Question 7
- Question 8
- Question 9
- Question 10
- Question 11
- Question 12
- Question 13
- Question 14
- Question 15
- Question 16
- Question 17
- Question 18
- Question 19
- Question 20
- Question 21
- Question 22
True-False Quiz
Determine whether the statement is true or false.
If it is true, explain why.
If it is false, explain why or give an example that disproves the statement.
Question 1
If u = <u1, u2> and v = <v1, v2>, then u ∙ v = <u1v1, u2v2>.
Solution: False
This is false, the Dot Product is a scalar and NOT a vector.

Question 2
For any vectors u and v in V3, |u + v| = |u| + |v|.
Solution: False
Consider the following example:

Hence, the statement is false.
Question 3
For any vectors u and v in V3, |u ∙ v| = |u||v|.
Solution: False
This false, as the formula needs a cosine function.
The geometric formula for the dot product is shown below.

Thus, the magnitude of the dot product would be:
|u ∙ v| = |u||v||cos θ|
Question 4
For any vectors u and v in V3, |u x v| = |u||v|.
Solution: False
This is false, the length of the cross product formula has a sine function in it.

However, for perpendicular vectors, the formula would be true.

Question 5
For any vectors u and v in V3, u ∙ v = v ∙ u.
Solution: True
This is true, and is a property of the dot product.

We can see this is the case:

Question 6
For any vectors u and v in V3, u x v = v x u.
Solution: False
This is false because the direction of the cross product follows the right hand rule, in which the fingers curl in the direction of the angle from u to v, and the thumb gives the positive cross product value.

Reversing the order of the vectors in the cross product would result in the thumb pointing in the opposite direction, hence the cross product will be negative.

Question 7
For any vectors u and v in V3, |u x v| = |v x u|.
Solution: True
This is true, since reversing the vectors in the cross product just gives a negative value, but the magnitude is the same.

Question 8
For any vectors u and v in V3 and any scalar k, k(u ∙ v) = (ku) ∙ v.
Solution: True
This is true and is a basic arithmetic multiplication property of the dot product.

We can see this is the case:

Question 9
For any vectors u and v in V3 and any scalar k, k(u x v) = (ku) x v.
Solution: True
This is true and is a basic arithmetic multiplication property of the cross product.

We can see this is the case:

Question 10
For any vectors u, v, and w in V3, (u + v) x w = u x w + v x w.
Solution: True
This is true and is another property of the cross product.

We can see why this is the case:

Question 11
For any vectors u, v, and w in V3, u ∙ (v x w) = (u x v) ∙ w.
Solution: True
This is true as it is a property of the scalar triple product:

We can see this is the case:

Question 12
For any vectors u, v, and w in V3, u x (v x w) = (u x v) x w.
Solution: False
This expression u x (v x w) is known as the Vector Triple Product.

Let's see if the given statement is true for the following example:
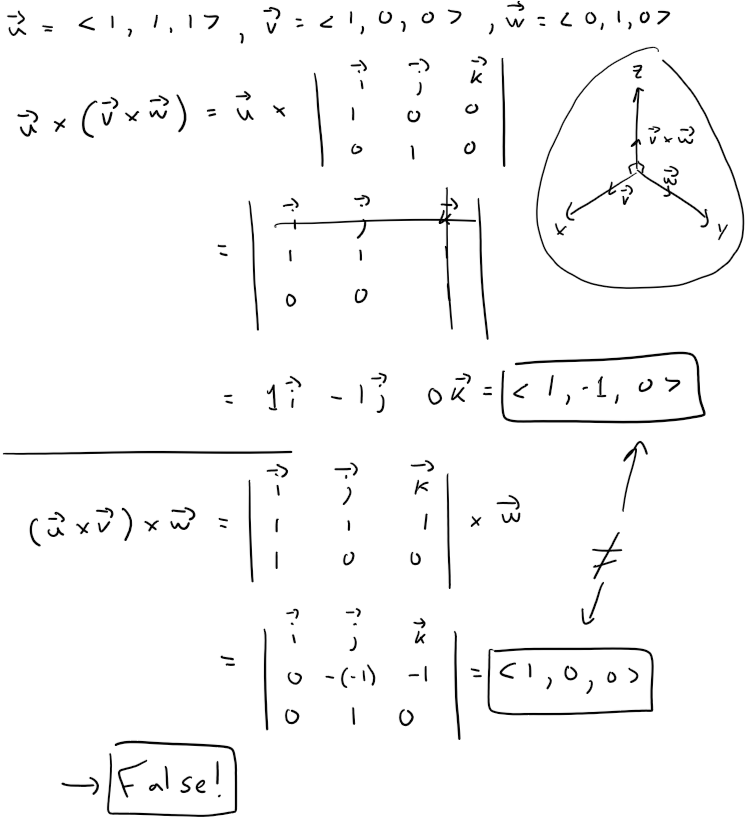
Thus the statement is false.
Question 13
For any vectors u and v in V3, (u x v) ∙ u = 0.
Solution: True
This is true because the cross product gives a vector that is perpendicular to both vectors, and the dot product between the cross product and one of its vectors is equal to zero if they are perpendicular to each other, which they are.


We can see this is true by computing the scalar triple product:


Question 14
For any vectors u and v in V3, (u + v) x v = u x v.
Solution: True
This is true because of the distributive property of the cross product (Question 10), and that the cross product of a vector with itself is equal to zero.


Question 15
The vector <3, -1, 2> is parallel to the plane 6x - 2y + 4z = 1.
Solution: False
The normal vector to the plane can be found in the coefficients of the linear equation of a plane.

The normal vector is <6, -2, 4>, and our given vector is just the normal vector divided by 2.

Thus the given vector is not parallel to the plane because it is parallel to the normal vector to the plane, that is, it is perpendicular to the plane.
Thus the statement is false.
Question 16
A linear equation Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 represents a line in space.
Solution: False
This is false, the linear equation represents a plane and not a line.
Question 17
The set of points {(x, y, z) | x2 + y2 = 1} is a circle.
Solution: False
This is false, the equation represents a circular cylinder.

We can also graph the cylinder in GeoGebra: https://www.geogebra.org/calculator/vgjh47g3


Question 18
In R3 the graph of y = x2 is a paraboloid.
Solution: False
This is false, the graph y = x2 in 3 dimensions represents a parabolic cylinder.

Graphing in GeoGebra, we can see that the equation is a horizontal parabolic cylinder: https://www.geogebra.org/calculator/vgjh47g3


Question 19
If u ∙ v = 0, then u = 0 or v = 0.
Solution: False
This is false because the dot product is zero if the vectors are perpendicular to each other regardless if one is equal to zero or not.
For example:

Question 20
If u x v = 0, then u = 0 or v = 0.
Solution: False
This is false because the cross product is equal to zero if the vectors are parallel regardless if any is zero or not.
For example:

Question 21
If u ∙ v = 0 and u x v = 0, then u = 0 or v = 0.
Solution: True
This is true because the dot product being zero means both vectors are perpendicular while the cross product being zero means both vectors are parallel.
This is only the case if one of the vectors is zero.

Question 22
If u and v are in V3, then |u ∙ v| ≤ |u||v|.
Solution: True
This is true because the geometric formula for the dot product includes a cosine function, whose absolute value is at a maximum of 1.


This is also known as the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality.


