~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
01-07-2024 - Energy systems - Real work cycle [EN]-[IT]
The factors that affect a real cycle
The actual duty cycle of a reciprocating volumetric compressor deviates from the ideal one.
This is due to several factors. In a real work cycle of a reciprocating volumetric compressor, situations come into play that are not considered in the ideal cycle. Below is a list.
Pressure losses along the ducts
At the valves the gas undergoes a series of pressure drops. Furthermore, the gas can also suffer leaks along the intake and delivery ducts.
Internal leaks
The compression and expansion of the residual gas contained in the dead volume are
real transformations characterized by internal losses.
Mechanical friction
The friction between the moving parts of the compressor leads to energy losses that are not considered in the ideal cycle. This mechanical friction originates mainly in the pistons and valves
Heat exchanges with the walls
The gas exchanges heat with the cylinder walls. In the case of an ideal duty cycle, the cylinder walls are considered to be adiabatic.
Losses due to gas leaks
Between the piston and the cylinder, there are seals and their imperfect seal means that the mass of gas actually sent to the delivery at each work cycle is lower than that sucked in.
Graphic
Below is the graph of a real work cycle of a reciprocating volumetric compressor.
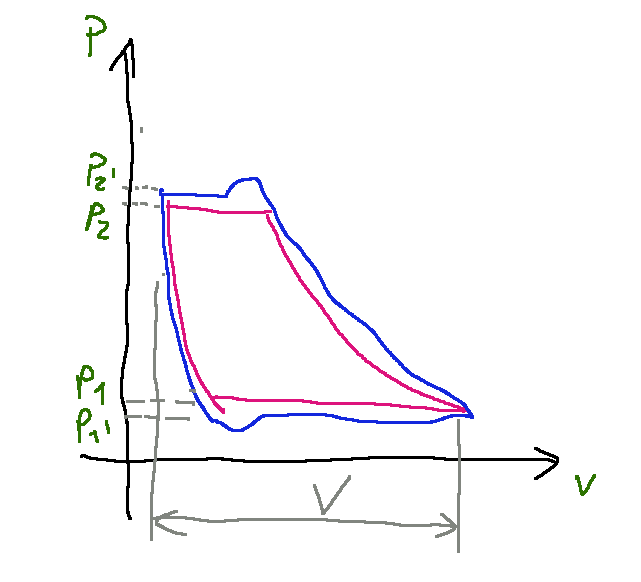
The red line is the ideal cycle, while the blue line represents the actual cycle.
Real duty cycle
In the real work cycle of a reciprocating volumetric compressor, the suction and delivery phases occur at a constant pressure as in the ideal case, but respectively lower and higher than the ideal case.
The compressor will work with a compression ratio which is usually expressed in the following way:
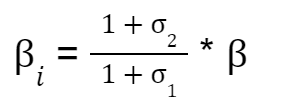
Conclusions
The expansion and compression phases are approximated with polytropic transformations.
Request
The differences between ideal cases and real cases have always existed in any topic of physics, do you prefer to study ideal cases or real cases more?

ITALIAN
01-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Ciclo di lavoro reale [EN]-[IT]
I fattori che incidono in un ciclo reale
Il ciclo di lavoro reale di un compressore volumetrico alternativo si discosta da quello ideale.
Questo è dovuto a diversi fattori. In un ciclo di lavoro reale di un compressore volumetrico alternativo entrano in gioco delle situazioni che non sono considerate nel ciclo ideale, qui di seguito un elenco.
Perdite di carico lungo i condotti
In corrispondenza delle valvole il gas subisce una serie di perdite di carico. Inoltre il gas può subire anche delle perdite lungo i condotti di aspirazione e di mandata.
Perdite interne
La compressione e l’espansione del gas residuo contenuto nel volume morto sono
trasformazioni reali caratterizzate da perdite interne.
Attrito meccanico
L'attrito tra le parti mobili del compressore comporta perdite di energia che non sono considerate nel ciclo ideale. Questi attriti meccanici hanno origine soprattutto nei pistoni e nelle valvole
Scambi termici con le pareti
Il gas scambia calore con le pareti del cilindro. Nel caso di un ciclo di lavoro ideale si considera che le pareti del cilindro siano adiabatiche.
Perdite per fughe di gas
Tra lo stantuffo ed il cilindro, ci sono delle tenute e la loro non perfetta tenuta fanno sì che la massa di gas effettivamente inviata ad ogni ciclo di lavoro alla mandata, sia inferiore a quella aspirata.
Grafico
Qui di seguito il grafico di un ciclo di lavoro reale di un compressore volumetrico alternativo.

La linea rossa è il ciclo ideale, mentre la linea blu rappresenta il ciclo reale.
Ciclo di lavoro reale
Nel ciclo di lavoro reale di un compressore volumetrico alternativo le fasi di aspirazione e mandata avvengono ad una pressione costante come nel caso ideale, ma rispettivamente inferiore e superiore al caso ideale.
Il compressore lavorerà con un rapporto di compressione che solitamente si esprime nella seguente maniera:
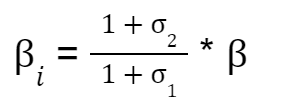
Conclusioni
Le fasi di espansione e compressione vengono approssimate con trasformazioni politropiche.
Domanda
Le differenza tra i casi ideali ed i casi reali sono sempre esistite in qualsiasi argomento della fisica, voi preferite studiare più i casi ideali o i casi reali?
THE END





