~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
23-11-2024 - Analytic Geometry - Affine Applications [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a short instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_68)
Affine Applications
Description
Affine applications and affinities generalize the notions of linear application and isomorphism.
We can also say the following. In analytical geometry, affine applications (or affine transformations) are functions that map points from one affine space to another, maintaining the fundamental geometric properties of figures, such as parallelism, length ratios along the same direction and collinearity.
Definition
A related application
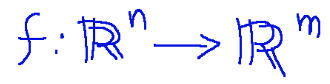
is a function of the shape
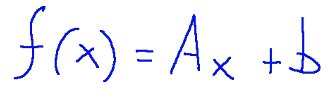
Where:

is the coordinate vector of a product in the starting space
A is an m x n matrix representing a linear transformation.
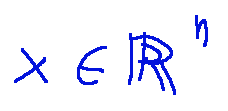
is a vector that represents a translation.
Some examples of similar applications
Translation
Translation is a transformation that rotates points around a fixed point:
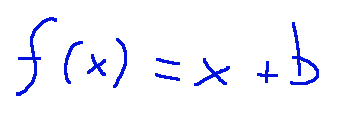
Rotation
Rotation is a transformation that rotates points around a fixed point.
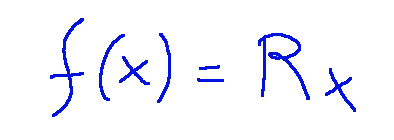
Where R is a rotation matrix
Concrete example of affine application
Let's consider the affine application
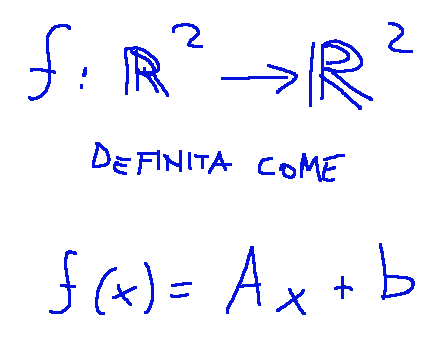
Where:
-The linear transformation matrix is
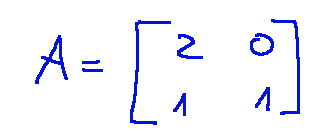
-The translation vector b is
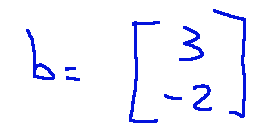
-X is the coordinate vector of the point in the space of start
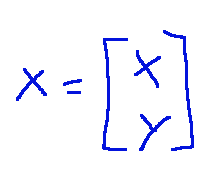
The application then becomes as follows:
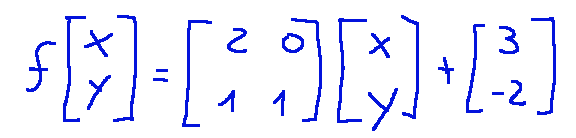
Explicit form construction
We perform the multiplication
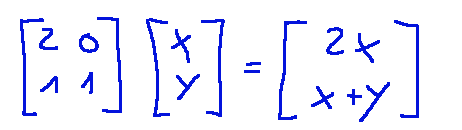
Now let's add the translation vector
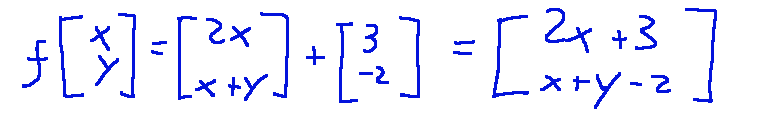
So we will find that the affine application will be the next:
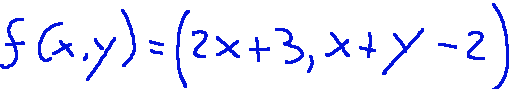
Conclusions
Affine transformations are fundamental in analytical and computational geometry because they allow to describe geometric modifications on figures such as translations, rotations, homotheties, deformations, etc.
Affine transformations are useful in computer graphics, modeling and image processing
Question
I find the concept of affine applications quite complex, is it the same for you?

[ITALIAN]
23-11-2024 - Geometria analitica - Applicazioni affini [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_68)
Applicazioni affini
Descrizione
Le applicazioni affini e le affinità generalizzano le nozioni di applicazione lineare e di isomorfismo.
Possiamo dire anche quanto segue. In geometria analitica, le applicazioni affini (o trasformazioni affini) sono funzioni che mappano punti da uno spazio affine a un altro, mantenendo le proprietà geometriche fondamentali delle figure, come parallelismo, rapporti di lunghezza lungo una stessa direzione e la collinearità.
Definizione
Un'applicazione affine
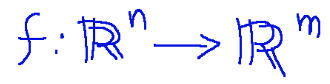
è una funzione della forma
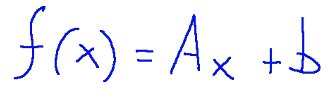
Dove:

è il vettore delle coordinate di un prodotto nello spazio di partenza
A è una matrice m x n che rappresenta una trasformazione lineare.
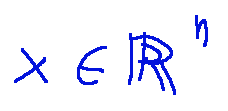
è un vettore che rappresenta una traslazione.
Alcuni esempi di applicazioni affini
Traslazione
La traslazione è una trasformazione che ruota i punti attorno ad un punto fisso:
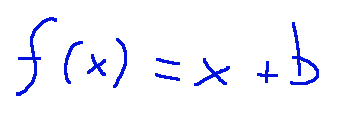
Rotazione
La rotazione è una trasformazione che ruota i punti attorno a un punto fisso.
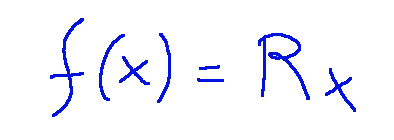
Dove R è una matrice di rotazione
Esempio concreto di applicazione affine
Prendiamo in considerazione l’applicazione affine
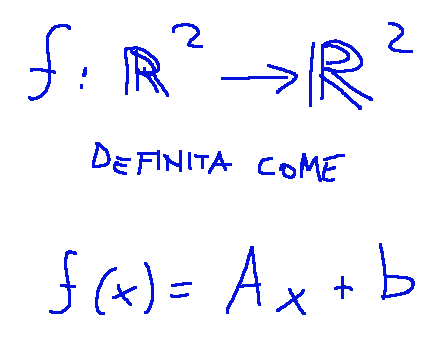
Dove:
-La matrice della trasformazione lineare è
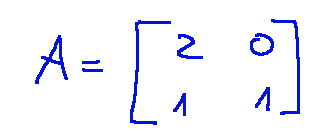
-Il vettore di traslazione b é
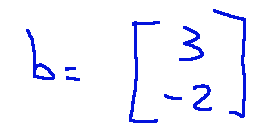
-X è il vettore delle coordinate del punto nello spazio di partenza
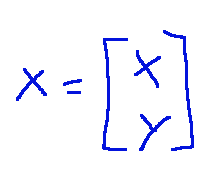
L’applicazione quindi diventa come segue:
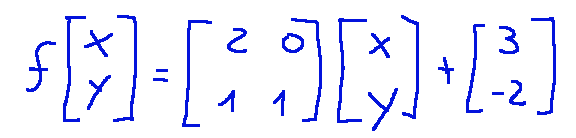
Costruzione della forma esplicita
Eseguiamo la moltiplicazione
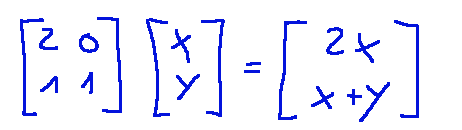
Ora andiamo ad aggiungere il vettore di traslazione
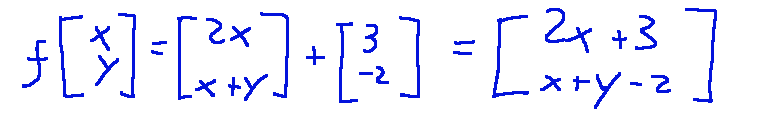
Quindi troveremo che l’applicazione affine sarà la seguente:
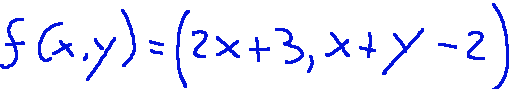
Conclusioni
Le trasformazioni affini sono fondamentali in geometria analitica e computazionale perché permettono di descrivere modifiche geometriche su figure come traslazioni, rotazioni, omotetie, deformazioni, ecc.
Le trasformazioni affini sono utili nella grafica computerizzata, nella modellazione e nell'elaborazione di immagini
Domanda
Io trovo il concetto delle applicazioni affini abbastanza complesso, anche per voi è così?
THE END