Blockchain and DLT are not the same, and blockchain is one of the methods used in DLT technology. In addition to the world-renowned blockchain, there are other ways to create a peer-to-peer system for transferring information and making transactions that can be used in widespread applications of distributed ledger technology. In this post, I will fully and comprehensively answer the question of what are the types of DLT.
What is a blockchain distributed ledger?
"Blockchain" is the most famous implementation of distributed ledger technology that is used in many digital currency projects today. Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger where transaction information is stored in the ledger as a chain of blocks. Blockchain can be viewed as a long list of transaction information. Information blocks in the blockchain can be used to store any type of digital information in the database, and its function is not only to record financial transactions.
To better understand the blockchain, we can use an example of a transaction log. Let's say someone is looking to make a transaction and send bitcoin or altcoin to a friend. In this case, a transaction is created from the user's side, which includes the time, date, amount and address of the recipient. The sender's information is also recorded in the transaction. In order to protect the privacy of users and not need authentication by a central authority, instead of the real name, "Digital Signature" is used to confirm the sender.
In this type of ledger, each block contains a special identifier called "Hash", which is used to distinguish each block and also to synchronize transactions. "Hash function" helps identify all transaction blocks in the ledger. The hash function includes numeric and alphabetic characters that are created randomly and uniquely from the input information, and it is not possible to reach the input from the output. In the following, I will explain more comprehensively how blockchain works.
How does blockchain work?
Blockchain is a set of interconnected blocks of information operated by a decentralized and distributed set of nodes. There are types of blockchain in private and public, and most of the focus of this topic is on its public type, which has greatly expanded the applications of blockchain. In general, we can examine the function of blockchain under the following topics.
- How to access the blockchain
- How to create transactions and confirm them
- How to reach a consensus to record information
- The reasons for the efficient operation of nodes
How to access the blockchain
Blockchain users can be divided into two general categories: "nodes" and "normal users". Nodes are responsible for verifying transactions, creating blocks, confirming blocks and adding blocks to the ledger, and are connected to the network through their network protocol software and hardware. Normal users are people who use blockchain to make transactions. Each user in the blockchain is identified by a public key to which the users' assets are attributed. The public key has its corresponding private key, which is similar to a password and only the user has access to it. The private key is used to access the account and spend assets and should not be shared with others.
Create a transaction in the blockchain
Normal users use digital wallets to record transactions. A digital wallet is software that creates public and private keys for users and connects them to the blockchain. To register the transaction, the user signs the address of the contact and the amount of the desired currency with the private key and sends it to the network.
Digital signature is a process in which the transaction information along with the user's private key is entered into the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) and produces an output. The desired transaction is broadcast among the nodes in the network so that all of them confirm the correctness of the transaction information.
Verification of transaction information is done in order for the nodes to make sure that the user has the amount written in the transaction in the account and that no one other than the original owner of the asset has sent the transaction to the network. To do this, the digital signature process is reversed. By plotting the digital signature, user's public key, and transaction information in elliptic curves, miners can verify that the information sent by the private key associated with the desired public key is signed or not. Balance confirmation is also done by checking user account information in previous transactions.

Consensus in blockchain
After confirmation, transactions are added to the Mempool or memory pool. Miners collect confirmed transactions and put them inside a block. The maximum size of each block is 1 MB. Now, one of these blocks must be added to the network and all users must agree on the desired block and update their ledger based on it. In order for this to happen without any problems, the consensus algorithm is used. Consensus algorithm is a method in which users show their honesty to the network by spending a fee and add new blocks to the blockchain.
If the consensus algorithm is not used, users can be randomly selected to add a new block to the network, but this method has many problems. If users don't need to spend energy and money to add a block to the distributed ledger, each user can define countless chances to create a block and cause the network to spam and fail. On the other hand, in the consensus algorithm, due to the existence of the reward mechanism, many nodes tend to work efficiently, which does not allow false information to be recorded in the blockchain.
Different types of consensus algorithms have been defined for blockchain, of which "Proof of Work" (Proof of Work | PoW) and "Proof of Stake" (Proof of Stake | PoS) are two famous examples. In proof of stake, by locking their tokens in the network, nodes get a chance to create a block in proportion to these tokens, and in case of malicious activity, they lose their tokens. The proof of work used in Bitcoin uses an advanced computational competition for consensus. The working method is that the nodes enter the input data of a block, including transaction information and the hash of the previous block, along with a random variable called nance, into a hash function and compare its output with the target hash determined for the block.
Nodes get the new output by putting different nance values in this function. Any node that can reach the target hash of the block before others will win the competition. The target node sends the block information to the network and users can confirm the validity of the claim of the winning node by entering the block and nonce information. After the block is confirmed, the nodes update their ledger with the new block, and the competition for the new block starts with the hash of the previous block and new transactions.
Why nodes work honestly?
Part of the honest activity of the nodes is due to the fact that the nodes themselves also operate as normal users in this network and the high security of the network ensures the security of their assets. But the main reason for the honest activity of nodes is the reward and punishment mechanism designed. Nodes in the Bitcoin network compete with each other to add blocks to the blockchain, and the result of this competition is the winner of the miner who obtained the network's target hash.
The target hash is designed in such a way that according to the computing power of all the miners in the network, extracting the block requires 10 minutes. This variable is known as "Network difficulty" or "mining difficulty". The winning miner receives both the newly generated coins and the fees paid by the users as a reward.
Each miner has a chance to win the mining competition depending on the computing power of the equipment, and for this they have to spend energy and time. Miners who do not have honest activity, the block produced by them will not be confirmed and will not receive any reward. As a result, the cost spent on buying crafts, the cost of electricity and the time spent on mining digital currencies are eliminated. In the Bitcoin network, the network reward is halved every four years, and after the end of the production of 21 million network coins, the miner's reward will be paid only with the cost of transactions.
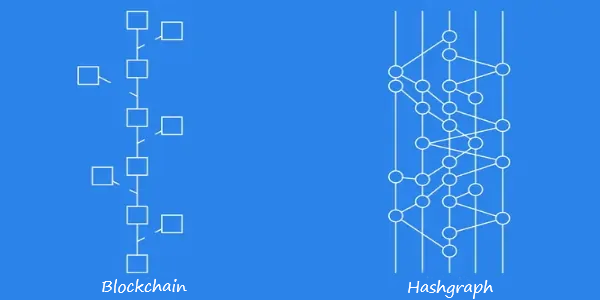
What is a Hashgraph distributed ledger?
The second type of distributed ledger technology is "Hashgraph". In the hash graph, multiple simultaneous transactions can be recorded in the distributed ledger because all transactions are kept in a parallel structure. Each record of transactions in the Hashgraph is known as an "event".
This type of non-blockchain distributed ledger is completely fair and no node in the network is able to manipulate information or transactions in it. This means that in a DLT system, no one can change the instructions being executed, and no user has the ability to delay events or change the course of transactions.
Compared to blockchain, this feature is quite remarkable. In blockchain technology, miners can add one of the two transactions in Mempool, which happened to be added to the network later than the other, to the new block. This system has been chosen in order to balance the amount of transactions and the cost of fees. However, in the hash graph technology, the nodes confirming the transactions are added to the network at the same time, and no transaction is left waiting outside the chain. In the hash graph distributed ledger, the faster the connection to the network and the transaction request is made, the transaction will be placed in the first line of approval and added to the ledger.
Why does Hashgraph need little memory?
In the hash graph implementation model of distributed ledger technology, all network transactions can be proven and confirmed. As soon as a transaction is done in the network, all the nodes present in the network recognize in which part of the ledger the desired transaction should be recorded. Additionally, everyone on the network knows that the transaction has been recognized by the entire network, allowing them to make the necessary changes to record the transaction.
This shows that nodes apply the changes resulting from a transaction to the distributed ledger before rejecting the transaction, and there is no need to store information indefinitely in the ledger. Because of this, the hashgraph distributed ledger database platform only needs a few gigabytes of memory to store all of its data.
The Byzantine nature of the hashgraph network
One of the main features of the DLT hash graph is "Byzantine". A Byzantine system is a system in which no group or entity is able to change the information sent in order to reach a consensus, and after consensus, no person is able to prevent this consensus. Every member of the network will know that a consensus has been reached on the network update, and the ledger will remain as agreed upon.
Each node in the network confirms how the transaction was performed and adds it in the same way in DLT without the blockchain structure. With this process, the entire community will have a unified distributed database system with similar features. If we compare with DLT blockchain, we realize that in blockchain the nodes of the network are never completely and 100% sure of the occurrence of consensus. This is the same feature that becomes possible in the hash graph.
How does hashgraph work?
The hash graph distributed ledger system uses the "gossip" protocol to broadcast all information, especially transactions, in the network. In this method, each network node can send information to others in a new transaction (known as event and pre-signed). Each node randomly uses its neighboring nodes to broadcast information. The node that received the information combines the event with another received data and sends it to other nodes in the neighborhood.
Therefore, when a transaction is performed in the hash graph, the nodes in the neighborhood share information with each other and others, and after a short period of time, all the nodes become aware of the transaction. Because this process happens quickly, every node in the network will be aware of the transaction within minutes. Finally, each node confirms the received transaction and then adds it to the ledger using the "Virtual Voting" protocol.
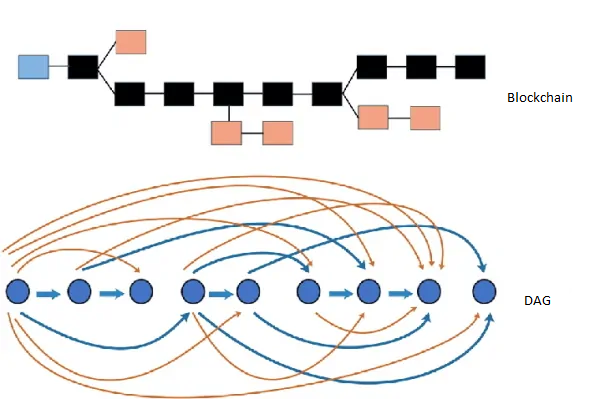
What is DAG distributed ledger?
The Directed Acyclic Graph, abbreviated as DAG, is the third implementation of distributed ledger technology, specifically used in the Phantom cryptocurrency project. DAG has been designed as a proposal to compete with blockchain, and as a result of this competition, it has been able to provide all the advantages of blockchain and improve some of these features.
Although DAG has been proposed as an alternative to blockchain, its structure is completely different from blockchain. One of the main advantages of DAG is the ability to perform microtransactions with close to zero cost. The reason for achieving such an advantage is the DAG structure, in which the more the network is used, the more the network's scalability increases. To understand how to do this, it is better to get acquainted with the working process of DAG.
How does Dag work?
Dag takes a different path compared to blockchain for the agreement and consensus of nodes in recording transactions and information. Dag's DLT system stores transaction processing in nodes. Like the blockchain, each member in the DAG network is called a node. All nodes in the network confirm transactions in the distributed ledger, and a valid transaction is backed by other confirmed transactions.
In the DAG structure, any node can initiate a transaction, but in order to confirm this transaction and send it to the network, it must confirm at least two transactions from the previous ledger transactions. After confirming the two previous transactions, the user's transaction will be confirmed. The more transactions a node approves (it means validating the transaction and confirming it if it is valid), the transactions sent by the user become more valid transactions. Therefore, the transaction with the longest branch of previous valid transactions will have the most weight in the ledger.
On the other side of the story, an algorithm is defined by the network that randomly selects the two previous transactions for confirmation by each user. This method makes users have to verify other people's transaction information and not just validate their own transactions. This issue is very effective in securing the network. This method is a very good way to achieve greater scalability through the consensus process. Companies and organizations that need a larger volume of transactions per unit of time can use this DLT implementation to record transactions.
What is the Holochain distributed ledger?
"Holochain" (Holochain) has presented the fourth version of the distributed ledger technology to users active in the field of cryptocurrencies. The main feature and difference of this method with the previous methods is the change of its approach from "Data-centric" to "Agent-centric". Holochain DLT has virtually unlimited scalability because it does not use a universal consensus protocol. The non-universality of the consensus protocol means that it is not necessary for all or the majority of network nodes to be involved in the consensus process.
The purpose of blockchain is to decentralize network transactions. Holochain also decentralizes the interaction of nodes with each other. Each node in DLT Holochain runs its own chain, which allows nodes to operate independently. However, each of these nodes is part of a larger network that includes thousands of nodes, and transactions between them are verified in a decentralized manner.
What are the special features of Holochain distributed ledger technology?
In traditional distributed ledger methods, all nodes in the network are forced to reach a global consensus in order to validate the information in the entire network. Holochain has changed this nature. The name of this distributed ledger implementation comes from the technology behind it, the hologram. In hologram technology, special light rays are needed to make a three-dimensional pattern, and the interaction with these rays is such that the desired image is created. Holochain follows a similar process and uses separate modules to create a ledger system.
In the Holochain project, each node maintains its own distributed ledger and communicates with this ledger through its unique signature. If we think of the distributed ledger of the entire network as a river, each of the distributed ledgers in the nodes is like a stream that flows into the river and creates the final ledger. In such a system, the offline of one of the nodes will not affect the ledger database, and other nodes will still create the main ledger by providing information.
How does Holochain work?
The working idea of Holochain is simple. Each node in this structure has its own distributed ledger, but all ledgers operate around a specific set of values called "DNA". Holochain's developers believe that this DNA ensures that any node trying to record new and correct information in the public ledger will be added to the network. In this system, a node sends information to other nodes and validates them, and if other nodes are able to confirm their information with DNA, they can broadcast this message to other nodes and validate them.
However, if someone tries to hack the network or add false data to the network, they will have a different DNA. Therefore, if someone tries to forge a transaction, they will disconnect themselves from the network. Other nodes in the network only accept users with DNA that has not changed compared to the past. As soon as differences are observed in a node's DNA, the nodes spread it throughout the network and inform others of the existence of a malicious node. This method is very practical and error-free, and because of this, it has been able to find many fans.
Is blockchain the same as distributed ledger?
Many digital currency market participants consider the term distributed ledger equivalent to blockchain. Blockchain is not the same as DLT, but it is one of the methods of implementing this technology, which was used for the first time in the Bitcoin network. Blockchain creates a secure distributed ledger for recording transactions and information using cryptographic techniques, a consensus algorithm, a reward system, and a specific protocol for adding blocks.
DLT is one of the basic terms in the world of digital currency, which is the main idea behind building a blockchain. The distributed ledger is a distributed and decentralized database whose security and efficiency are provided by encryption techniques and consensus algorithm among network operators.






