
Introduction
What exactly is the definition of an asset??
According to Investopedia---
An asset is anything of value or a resource of value that can be converted into cash.
An asset that can be converted into cash(monetary value), which means it's tradeable. Trade can be facilitated by an Exchange platform.
If Blockchain has redefined how should we own the asset(absolute control), then DEX tells us how should we exchange the asset(Decentralized-- Algorithmic Smart contract). If Blockchain is Layer 0, then DEX can best fit into Layer 1, and Layer 2. So a DEX ferry into dynamic decentralized usage, honoring the basic principles of Blockchain.
An asset is relevant to us because of its economic value. Crypto itself is a quantifiable form of thing we value or we consider valuable. For instance, socializing was having no value(monetary) until the advent of crypto powered with Blockchain technology.
An asset matters because it has a certain economic value. Similarly, a DEX matters because it furthers tells us how we use this asset in space and time for a certain purpose.
DEX as opposed to CEX is decentralized. Like asset, like usage. Crypto stands on a sub-structure of a decentralized base(Layer 0), making it trustless, and therefore it embodies trustlessness.
Today we are more interested in crypto or likes of crypto because it entails absolute ownership of the asset.
What exactly do we do with this asset, we acquire it and store it(Store of Value). When we store it we certainly use a decentralized wallet. Because that is how we can ensure trustless ownership, self-custodian wallet, or absolute ownership.
The objective as envisaged in the basic principles of Blockchain is not just a decentralized wallet, but rather a whole ecosystem of a decentralized environment. Therefore the true objective of crypto can be achieved not just in a static decentralzied wallet, but also in its dynamic behavior/usage.
What exactly does dynamic behavior/usage mean?
At any given space and at any given time, crypto whether static(in a decentralized wallet) or dynamic(exchanging, trading, staking, etc) should be held or executed in a decentralized way.
Smart contracts joined the bandwagon in 2014 but their extensive use started taking off in 2020 with the proliferation of DeFi.
So the dynamic usage of crypto has been aided by smart contracts and we have seen how Web 3.0 is slowly making inroads in everyday endeavors-- be it social or economical.
In light of the Decentralized Environment, let's discuss how and why does it(DEX) matter?

Decentralized Exchange
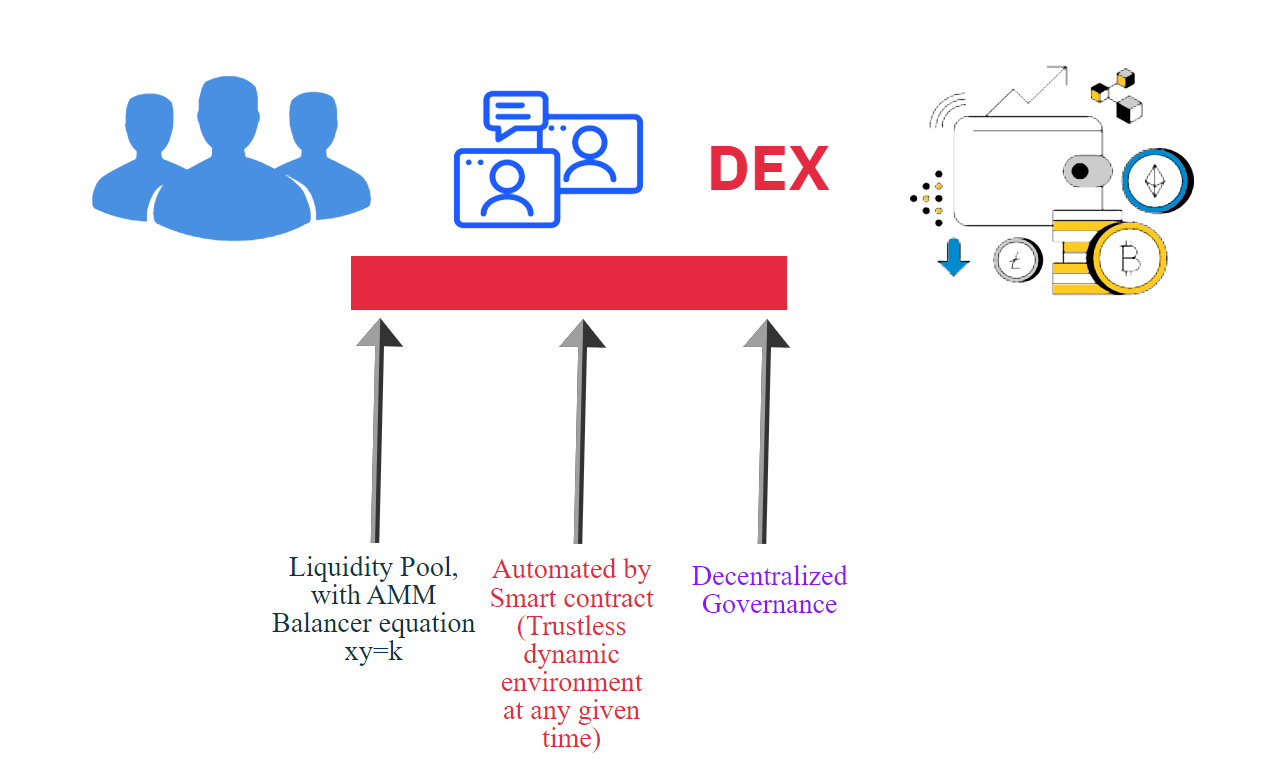
Without going into its technical details, let's see what are the three pillars of a DEX in the context of its usage:-
(i) Liquidity Pool, with AMM Balancer equation xy=k
(ii) Automated by Smart contract (Trustless dynamic environment at any given time)
(iii) Decentralized Governance
At times, it is misunderstood that the governance part has less to do with what end-user wants as an exchange facility in DEX. But the reality is that a DEX sustains in the long run because of its decentralzied governance, DAO, etc. Otherwise, the decentralized ecosystem has also a tendency to degenerate into a centralized ecosystem in the long run without checks and balances.
(i) Liquidity Pool, with AMM Balancer equation xy=k
The very basic thing of any exchange facility is its liquidity. In centralized exchange if there is a shortage of liquidity you won't get a competitive value of your exchange or the exchange may not be possible at all.
In DEX, liquidity also plays a vital role, but with the advent of AMM-based DEX, the liquidity issue of DEX is solved by AMM balancer equation xy=k.
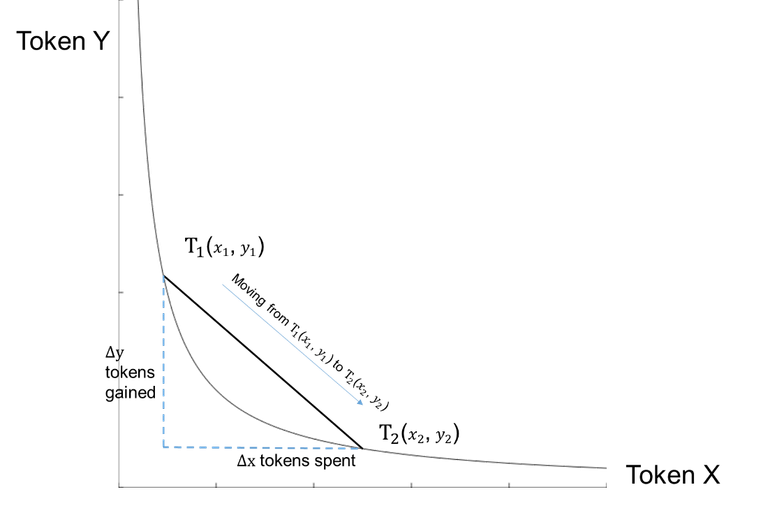
xy=k: source
Any trade or exchange is exemplified by a pair. The x and y are the two sides of that pair. Why is it called a balancer equation? Because the algorithm is set in such a way that value on both sides at any given time should be balanced. If it is unbalanced externally, then it creates a lucrative arbitrage opportunity to invite traders and correct it at par with the border market value.
The DEX makes it open-ended for all, which implies that anyone can contribute to the liquidity pool(democracy), and a liquidity provider is entitled to a share of the exchange fees in proportion to his contribution.
Definitely, there are two types of players in a DEX and both complement each other. DEX or the likes of DEX are maintained by the spontaneous action economic element of society. In a market society, the spontaneous order/action of liquidity provider and trader/exchanger adjust with each and fulfill each other's requirement in a myriad of transactions making it more fluid, ubiquitous, and stable.
(ii) Automated by Smart contract (Trustless dynamic environment at any given time)
The smart contract is arguably the actualizing force of web 3.0. For fintech and DeFi, web 3.0 is a necessity, so DEX operation is unimaginable without automated smart contracts. This is also vital to create a spontaneous economic order.
Every time a trader interacts with a DEX(liquidity provider or exchanger) the interaction/engagement sets off algorithmically using smart contracts. Every record of interaction/transaction is verifiable-- Transparency and Absolute authority.
Since it is operated by Smart contract there is no scope for any KYC or KYC-obliged compliance. So a user does not face any restriction on the ground of KYC or sensitive private data sharing. A web 3.0 wallet(key-based wallet) is the only requirement to engage with a DEX.
(iii) Decentralized Governance
Leading DEX like Uniswap started this culture of decentralized governance in DEX. This is also essential to sustain the ethos of DEX environment in the long run.
Most of the time, we value crypto on the basis of its immediate monetary value or store of value. But crypto is also a form of governance token. The whole of idea of quantification stems from the idea of giving ownership rights of this decentralized environment to its people so as to foster a sense of community.
The use of crypto with the capacity of governance token emerges when you vote a proposal, vote a witness, or delegate power to those who run the things.
Most DEXs these days are issuing their own protocol token. And participants are earning protocol tokens in a variety of ways(liquidity provider, airdrop, staking, etc).

Shortcomings of DEX
DEX is an expression of the economic order in the crypto ecosystem, they are the expressions because they offer that dynamic decentralized space to crypto in the use-case like how we use it-- how we trade it, how we lock it. At any given space and at any given time they are executed through algorithmic smart contracts.
But like any other thing, DEX has its shortcoming also.
(1) It is always advisable to trade with an amount less than or equal to 1% of the liquidity size in AMM-based DEX. Because if you trade higher than this size, it might become cost-prohibitive. Suitability for a whale depends on the liquidity size of the pool of a particular pair.
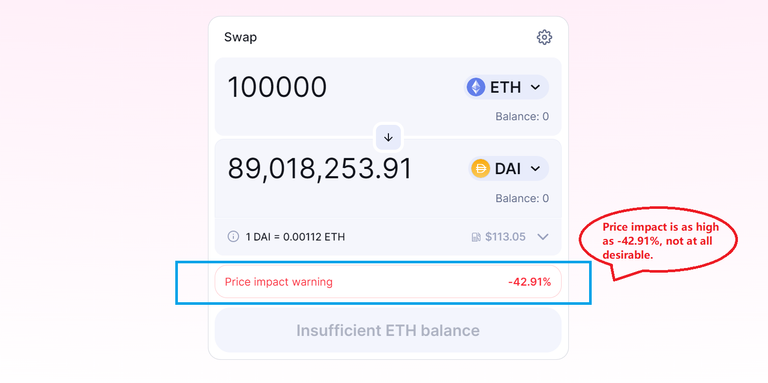
Uniswap: source
(2) A liquidity provider may suffer impermanent loss. Please note that it is impermanent, i.e. not permanent. For instance, if the traders keep trading on one side one after the other, externally it may create arbitrage opportunity but internally it will make one side scarce and the other side abundant.
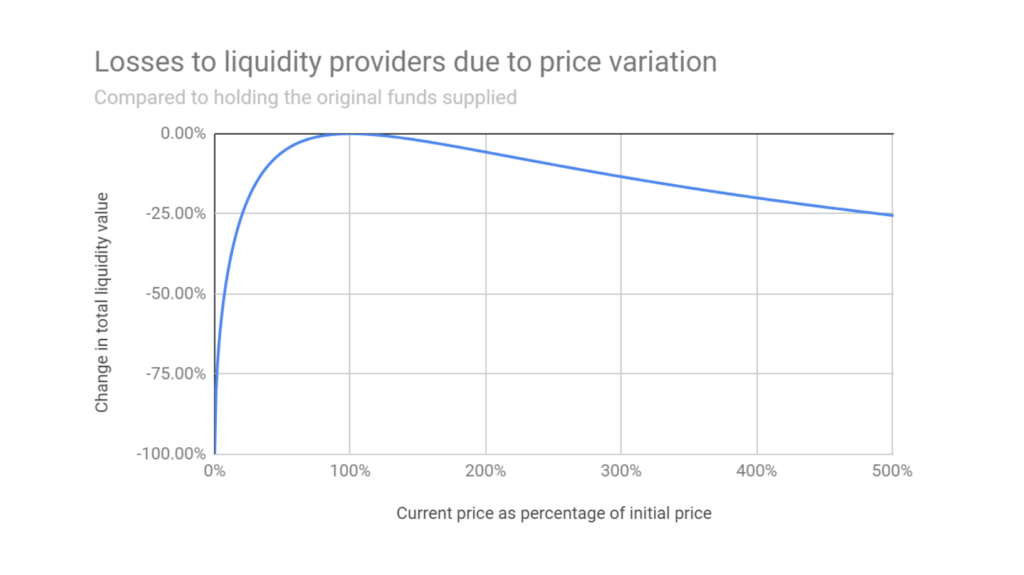
Impermanent Loss: source
Of course, it will not affect the value of the total asset but it will change its composition. In any case, the exchange fees share which is continually being accrued generally offset such loss for a liquidity provider. So unless you unstake it or withdraw from the liquidity pool you won't realize this loss.
(3) AMM-based DEX does not have an order book model, so you may not be able to set your SL or you may not be able to set a pin-pointed trade. There will be a certain slippage, although this slippage is very low and you can also set the upper limit of the slippage, beyond which it does not get executed.
(4) Exchange fee. The smart contract-based operation certainly consumes more gas fees than normal transactions. So it may not be suitable for micro traders who trade less than 10 USD. However, there are several cost-effective low gas fee-based chains have evolved like BSC, Matic, and many others with wrapped versions of the token. So as of today, we have more options to weigh upon.
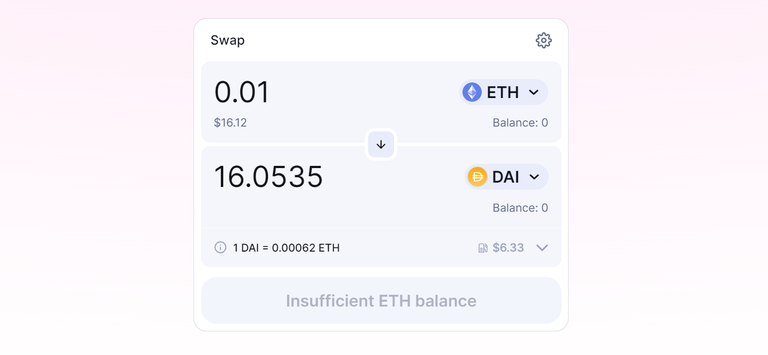
Uniswap: For an exchange of 0.01 ETH to DAI which is approx $16 trade the gas fee is as high as $6.33, which is almost 38% of the trade value, not at all cost-effective for a micro trade. source
(5) For a naive user, the downside of DEX is that he might not be able to approach a customer care representative for immediate queries and redressal. That is a facility generally available in CEX only.

Summary(Why does it matter?)
It matters because it offers decentralized space at any given time during the exchange, trade, locking, or any other DeFi operation.
It does not impose KYC-obliged compliance on its users.
Both static(wallet) and dynamic(exchange) decentralized space are in line with the principles envisaged by Blockchain technology.
It passively promotes web 3.0 uses because web 3.0 is the actualizing force of any AMM-based DEX.
It creates a spontaneous order of human relationships and invites people to join as liquidity providers to help the rest of the users who wish to be a trader. By doing so it becomes self-serving as well as creates a just economic order by allowing uncensored unrestricted myriad transactions at any given time.
The overall benefits clearly outweigh its shortcomings. The balance of benefits over its shortcomings has produced a tectonic shift not only in how we own the asset(decentralized), but also in how we use the asset(decentralized), and to make this a reality DEX proves to be a vital link in proliferating the basic principles of Blockchain technology.

Note- Unless otherwise stated, all the infographics are created by me using suitable tools/applications.
Disclaimer:- This article is intended for educational and analytical purposes only. It should not be construed as financial advice. Thank you.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
