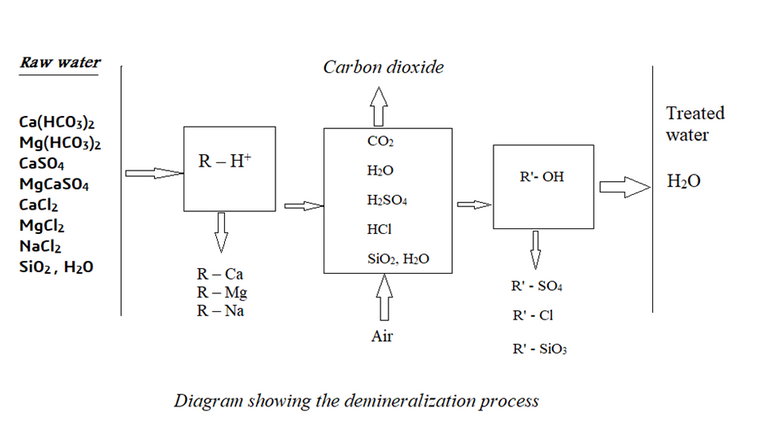
The field of treating drinking water does not employ this technique; rather, it is used in the industrial sector. Three fundamental steps make up the demineralization of water:
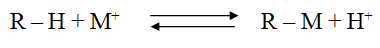
1- Positive and strong-acid ion exchangers are used to remove positive electrolytes, and strong mineral acids are then used to refresh the system. The following equation explains the exchange mechanism:
[Made using Microsoft Word]2- Aeration is used in the second stage to remove carbonates and carbonic acids. The operation is carried out by the water falling from the first exchanged column into the ventilation column in the shape of a waterfall. The ventilation column has an air source at the bottom that is discharged into the descending liquid to give it a high contact surface. When carbonic acids dissolve, free carbon dioxide gas is released into the atmosphere, which rises inside the column. For the decomposition of carbonates and carbonic acids into carbon dioxide gas and water, a favourable environment is created by the hydrogen ion liberation, which creates an acid medium.
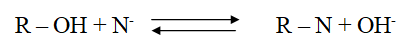
3-In the third step, negative electrolytes are eliminated using a powerful alkaline negative ion exchanger that is refreshed with sodium hydroxide. The exchange mechanism is represented by the following equation:
[Made using Microsoft Word]A extremely pure water with a specific resistance of more than 0.3 MΩ/cm is what we get at the third stage's conclusion.
[Made using "Paint"]
Components and equipment of the ion exchange demineralization unit:
Raw water inlet- Flow meter- Acid inlet- Metering pump- Countercurrent regeneration positive ion exchanger- Carbon dioxide removal tower- Tower aeration fan- Pump- Weak alkaline negative ion exchanger- Strong alkaline negative ion exchanger- Treated water basin- Ohmmeter- Sample socket- Standard pump for sodium hydroxide solution.
References:
- [Introduction to Water Chemistry (Pollution- Treatment- Analysis). Dr. Nasser Al-Hayek. Publication of the Higher Institute for Applied Sciences and Technology (HIAST). Syrian Arab Republic, 2017.]
- Taparhudee, Wara (2002). "Applications of Paddle Wheel Aerators and Diffused-Air System in Closed Cycle Shrimp Farm System" (PDF). Witthayasan Kasetsart (Sakha Witthayasat). 36: 408–419. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- Unsafe water kills more people than war, Ban says on World Day". UN News. 22 March 2010. Retrieved 10 May 2018
- Raymond Desjardins- Livre: Le traitement des eaux- 2éme edition- Ecole Polytechnique de Montréal- 1997- ISBN 2-553-00643-8
- Drinking Water Treatment- EDX- Delft University of Technology.
- Book- Drinking Water: Principles and Practices- by Hans J C Van Dijk (Author), Jasper Q J C Verberk (Author), Peter J De Moel.



