In the last post, we looked at how imagining can give insight into mood disorders but has not been diagnostically significant. We saw some metabolic changes that could be seen with PET.
We also finished up with the study we had been looking at and they the limitations to the study and why the crossectional study may not be a picture of the world's BAD. There were also some things that connected this study to world standard studies.
We looked at behavioural studies and why they are not s very effective choice for doctors,
Inkscape.org
Depression vector created by pch.vector - www.freepik.com and
Welcome to Medic Vibes, where we discuss mental health disorders and make sense of them. Dr Ebingo Kigigha is a medical doctor (aspiring psychiatrist) and creative person (illustration and music). This has been our routine for two consecutive months. This month will be dedicated to BAD or Bipolar Affective Disorder. In the first month, we discussed Depression, and in the subsequent month, anxiety. We are done looking at a Nigerian study and now we are moving to Twitter posts.
Announcement!!!
We are moving to our new account after this months topic. Follow us here @medicvibes
In this post, we are looking at this tweet that talks about some of the comorbidities of BAD. I really hope his mom is getting better. Above we have talked briefly about the comorbidities of BAD, but for this post, I was hoping we could go through them thoroughly.

Patients who are bipolar have these major depressive episodes and manic episodes. Mood disorders are also called affective disorders 2 months ago, we talked about depression, among the types of depression is Major Depressive Disorder which is otherwise known as unipolar depression.


Top Left King Saul, Top Right Hippocrates Bottom Left Robert Burton Bottom Right Anatomy of Melancholy
History
King Saul's features in the bible, were typical of mood disorders when he would have David play for him in his palace. Hippocrates believed depression was a result of black bile and he called it Melancholic (meaning Black Bile). The first person to describe depression in English text was done by Robert Burton. His book Anatomy of Melancholy dates back as far back as 1621. Emil Kraepelin developed the criteria that is still used for manic-depressive psychosis. It was called folie circularie.
Demographics
Among all the mood disorders BAD I has the earliest onset. The prevalence of BAD I is equal in men and women. Episodes of mania are seen more in men while depressive episodes occur more in women. Depression appears to have a higher occurrence in rural areas, there is a tendency for schizophrenia to be misdiagnosed by practitioners from a different culture from the patient.
Other Associated Conditions
People who deal with mood disorders are significantly at risk of dealing with alcohol abuse or dependence, anxiety disorders particularly panic, obsessive-compulsive and phobias, particularly for people and socialising. Women particularly have eating disorders when they go through unipolar and bipolar disorders. Biogenic amines affect the concentration and effect of the neurotransmitters at the synaptic cleft. Cholinergic agonists modulate the activities of the pathway between the hypothalamus, Pituitary gland and adrenal gland. GABA inhibits the action of monoamine pathways that ascend especially the mesocortical and mesolimbic.
NMDA receptors bind to a receptor called N- methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) when there is excess stimulation it leads to toxic effects on the nervous system. This may be because of the effect of glutamate's function in working against neurocognitive decline seen in recurrent severe depression as well as hypercortisolemia. Some drugs that act to synergise with GABA have a noticeable but insignificant antidepressant effect. Patients whose mood disorder is remitting and those that have close relatives have a trait that resembles the sensitivity to cholinergic agonists.
Alterations in Hormone Regulation
The studies were done with Urinary Free Cortisol, 24 house intravenous taps for plasma cortisol, cortisol in saliva and a test of feedback inhibition. There are known documentation about the changes in hormone interplay in the brain and reactions that can be a result of early life stressors. Early trauma can lead to increased hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal(HPA) activity which is followed by cerebral cortex volume depletion and cellular reduction. HPA activity is being referred to as a clear feature of mammalian stress and it is a link between depression and the biology of chronic stress. 60% of the time cortisol is not suppressed in the morning or it escapes suppression by 4 pm.
This test does not provide a diagnosis for mood disorders because the same results are seen in mania and other psychiatric conditions. 5 to 10% of those who are depressed usually have a thyroid abnormality, this is seen in the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone or the fact that there is an abnormally high reaction to 500 mg of hypothalamic neuropeptide thyroid releasing hormone. Prolactin is a hormone released in response to serotonin stimulus and inhibited by dopamine stimulus. So far there has not been any major correlation between prolactin and depression.
There are associated sleep patterns in depression The characteristics of this easy arousal are longer periods of nighttime awakeness, reduced sleep time, an increase in the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) phase of sleep and a rise in body temperature. Reduced secretion of growth hormone is linked with this reduced slow wave sleep. In 40% of outpatients with depression and 80% of inpatients, it is seen. This is because there is increased REM drive and reduced fast-wave sleep that results in a reduced first period of non-Rapid Eye movement (NREM). There is a reduction in REM latency this is because there is increased REM drive and reduced slow wave sleep that results in a reduced first period of non-Rapid Eye movement (NREM).
Imaging in Mood disorders
The areas being studied are the cortex, subcortex and areas of white matter. These hyperintensities are seen more frequently in BAD I and elderly patients. They are evidence of neurodegenerative affectation of the brain due to mood disorders. What has been observed in depression is an increased occurrence of hyperintensities in the subcortical region.
Neuroanatomy
There is enough evidence from the symptoms and research results that mood disorders emanate from brain pathologies. There are 4 regions in the brain that modern medicine believes are the seat of emotions. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), the anterior cingulate, the hippocampus and the amygdala.
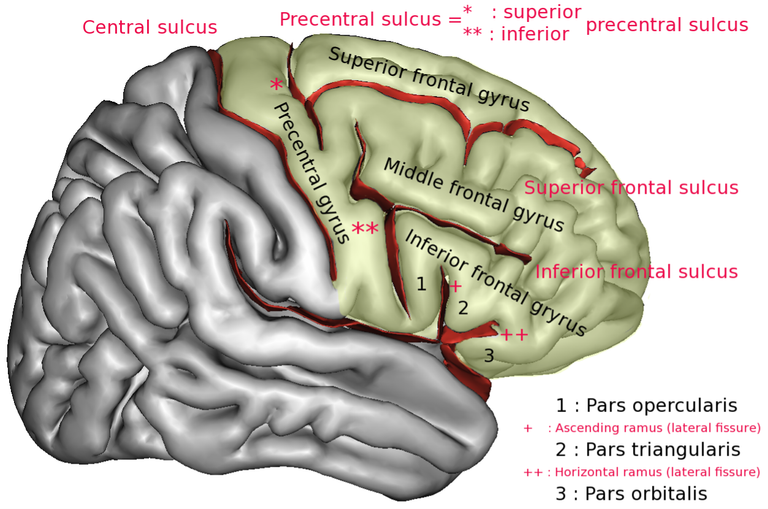
The PFC is believed to be the knowledge of what a goal is and what is needed to be done to attain these goals. Considering that the road to achieving the said goal may be numerous, sometimes oppose each other or may require forgoing pleasure it is easy to see how important this part of the brain is. There is proof that the two hemispheres of the brain show differences in this particular function, where the left is involved directly with goal achievement and moving towards a specific appetite, and the right side is more involved with inhibitions and avoidance. Specific areas of the PFC are involved with reward and punishment.
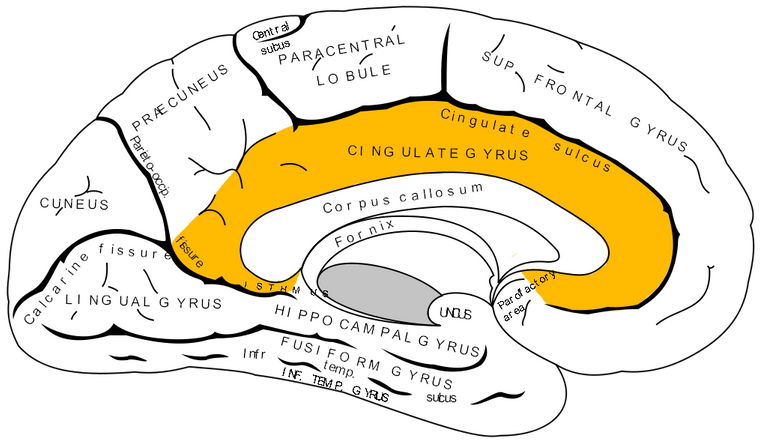
The Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC) Is viewed as a focus of efforts for motivation. There are two divisions of the ACC. The first part is the affective ACC and the second part I the cognitive part. The affective part is well connected to the limbic region. The cognitive part is connected to the PFC and other cortical parts of the brain. The ACC is believed to control emotions when stimulated especially when goals become harder to accomplish because of problems.
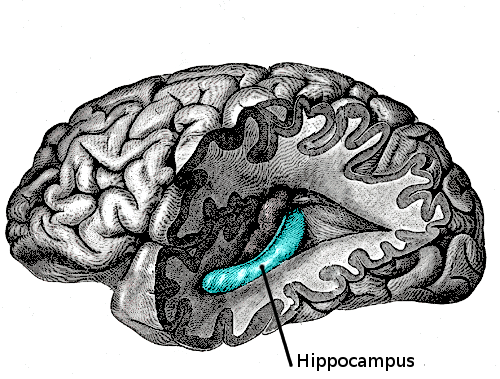
The Hippocampus
The Hippocampus’ responsibility in learning and memory, fear regulation and its part in inhibiting the Hippocampal Pituaitarty adrenal axis is most well known. A type of learning known as emotional learning is bright about from a link between the hippocampus and amygdala.
The amygdala is very instrumental in assessing new information that is emotional significant and telling the brain’s cortex how it is supposed to respond. It has been described severally as the heart of the limbic system and is located just above the amygdala. Most of what we know is from research about the amygdala in fear and pain but new information may be the trigger for this part of the brain rather than the associated fright of the situation.

Comorbidities
Those who suffer from mood disorders can also deal with some additional problems, particularly related to mental health. Among the most common are alcohol addiction and substance abuse, others are related to anxiety disorders. The tweet contained evidence of this however, the particular anxiety disorder that was talked about was PTSD. Which is not a very common presentation.
The more common anxiety disorders that are associated with BAD are panic disorders, Obsessive Compulsive Disorders and Social Anxieties.
Inversely, anxiety disorders also have an increased risk of mood disorders as a complication.
In terms of sexes, it is more common to find a man dealing with substance abuse and women will experience anxiety disorders and eating disorders.
When compared to unipolar depression those with bipolar disorder have a higher tendency to be affected by substance abuse.
When a patient starts abusing substances it makes it harder to treat the mood disorder and those with unipolar depression are at significant risk of suicide.

Tips
I was considering giving tips about PTSD, but seeing as that is a less common comorbidity I thought I should go for Alcohol-induced mood disorders which are more common.
When Alcohol is consumed In in high amounts over many days it can make a patient start having symptoms that are seen in mood disorders especially major depression.
This must be however not the same thing as major depression because the symptoms are tied to the use of alcohol and usually go away when the patient is abstinent.
This is the case for almost 80% of people, chronic drinkers. The depression lasts for 2 weeks or more 30 to 40% of those who reported using alcohol this way. But just above 10% of them will ever meet the criteria for major depression when they never abused alcohol.
Even if it is a severe case of substance abuse depression, the case is likely to get better very quickly once the person stops using. They do not require drugs or psychotherapy.
The best way to deal with this condition if you are facing it is to learn to deal with moments of sadness and possibly seek Cognitive Behavioural Therapy. This is typically done for about 2 to 4 weeks before commencing antidepressant drugs.

Hive Stories
@garybilbao from the lotus community talks about his depression and draws light to the topic. In this post, are some of the causes of depression and it also included alcohol abuse as a cause.
Read this post here
Questions
- What did you learn about mood disorders?
- What did you learn about Bipolar disorder?
- What did you learn about the comorbidities of Bipolar disorder?
Conclusion
In this post, we were able to see some anatomic figures in moods. They include the PFC, the amygdala, the ACC, the hippocampus and the amygdala.
We discussed a Twitter post that had a lot to do with comorbidities and saw that although PTSD was not a very common comorbidity anxiety disorder as a whole.
We revise some treatment tips for one of the most common comorbidities in mood disorders which is alcohol abuse.

I hope that you learned a lot from this post.
To book me for illustration gigs click Here
References
- Kaplan-Sadocks-Comprehensive-Textbook-Psychiatry
- Page demarcations made with Inkscape.org