Hello everyone, nice to meet you all again. How are you? and i hope you all are doing well. i am loaded with my work but i got time to share with you. Today i would like to share tuberculosis of lung. How it looks like in Lung? lets discuss with a case.
Case History
A 43 year old male patient who is known case of carcinoma of lower esophagus and CECT of lung was done and the radiology reports says T7 to gastroesophageal junction soft tissue thickening of lower 1/3rd of esophagus with multiple bilateral lung nodules with some of them showing calcification and associated adjacent fibrosis-probably infective, less likely mets.
core biopsies were taken from right apical lung nodule andsent in formalin to histopathology.
so this is case history of the patient and we received the sample and we did grossing, tissue processing and everything and finally we got slides.
Under microscopy these are the things that i have seen and i captured them.
4X magnification
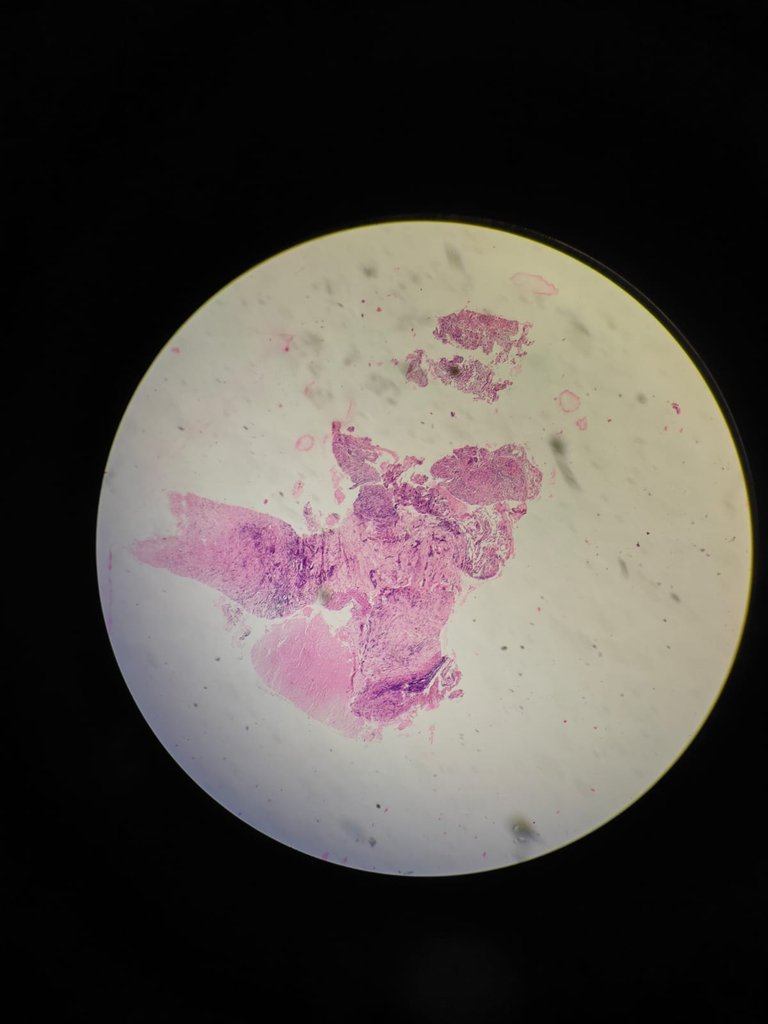
At 4X you can see there is pink area which is necrosis. In TB, we will see caseous necrosis.
10X magnificaton
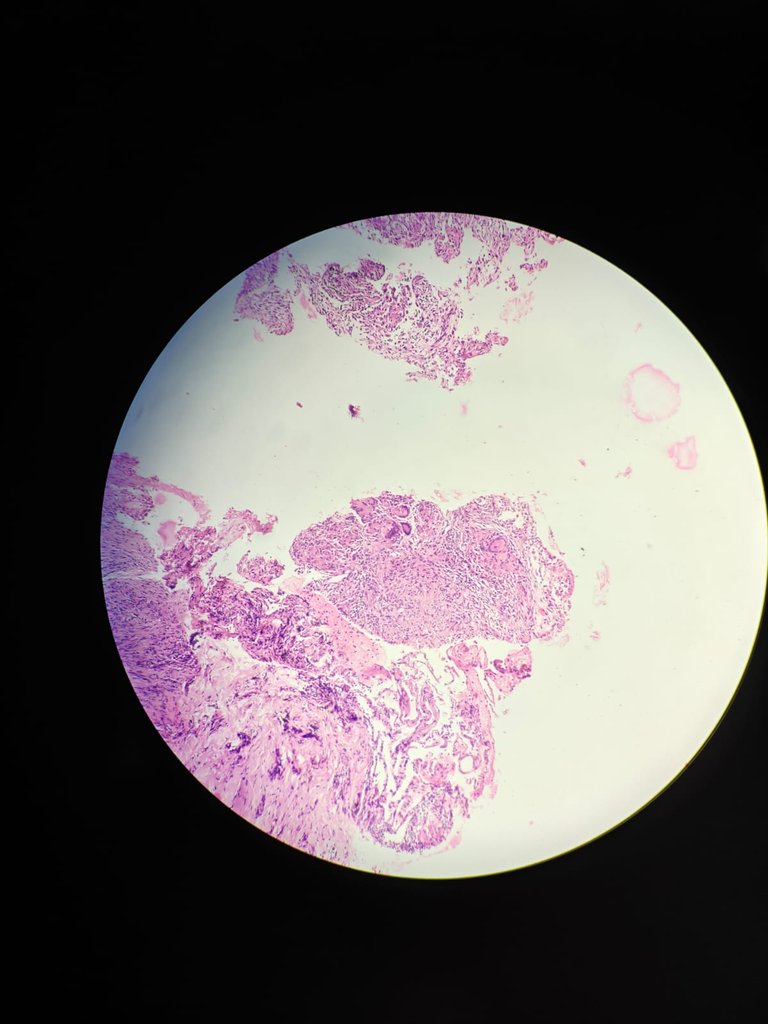
20X magnification
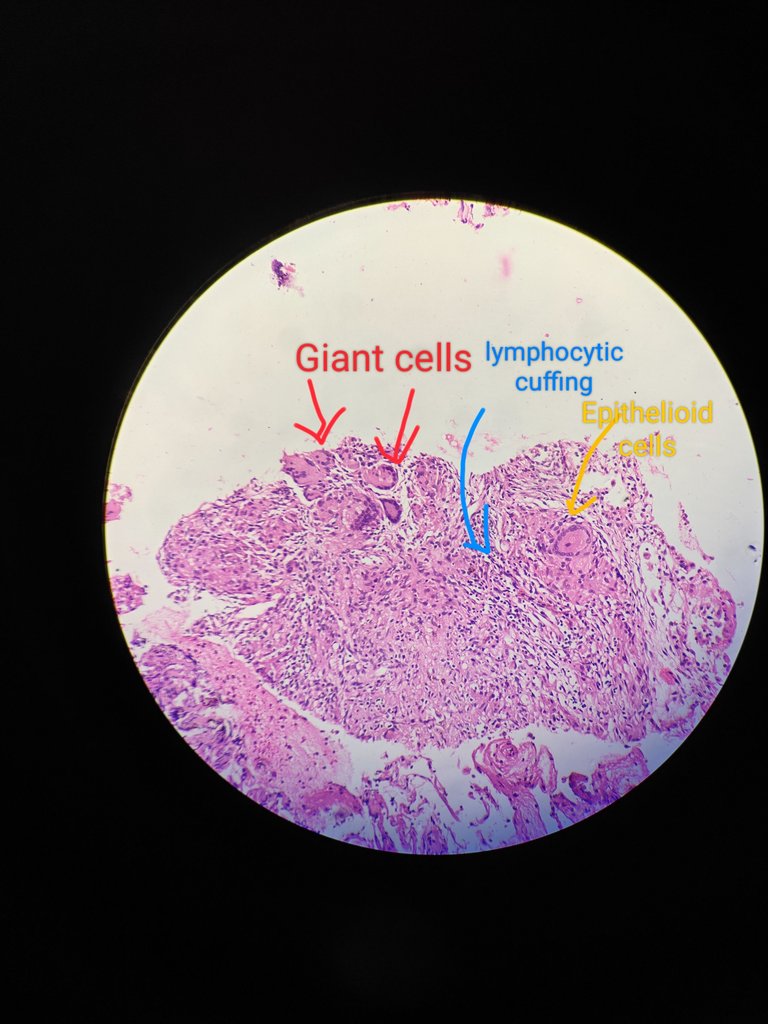
At 20X we can see that there are langhans giant cells(horseshoee shaped) and epithelioid cells(modified macrophages) and lymphocytes. So if we see these things then its called GRANULOMA.
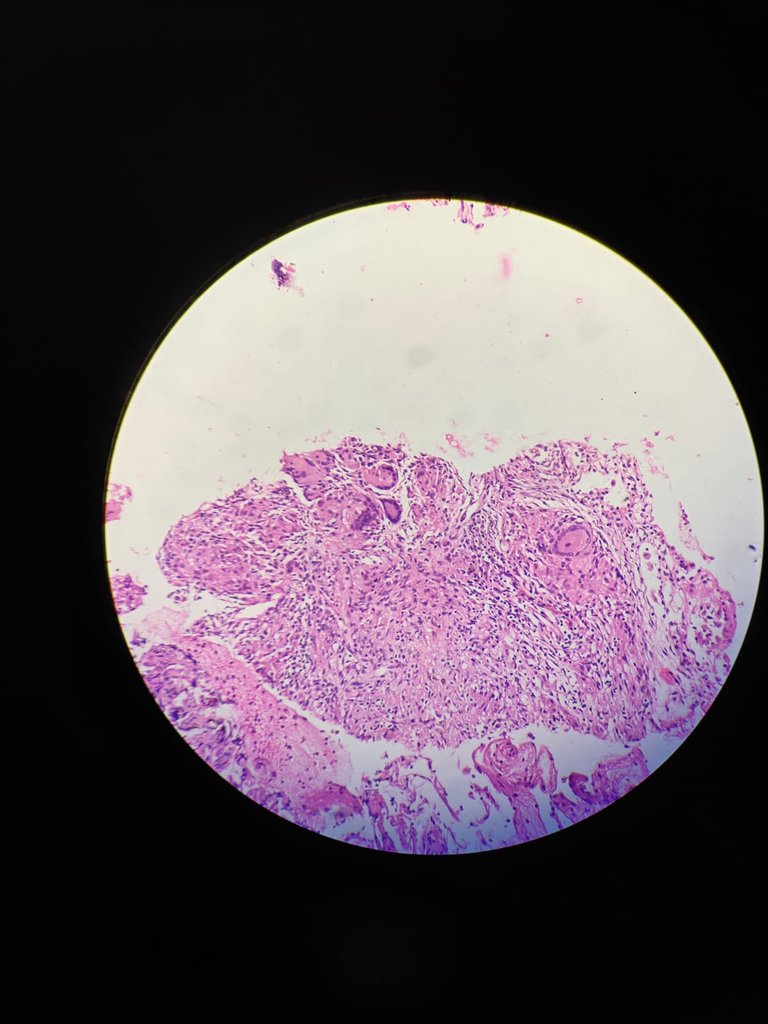
40X magnification
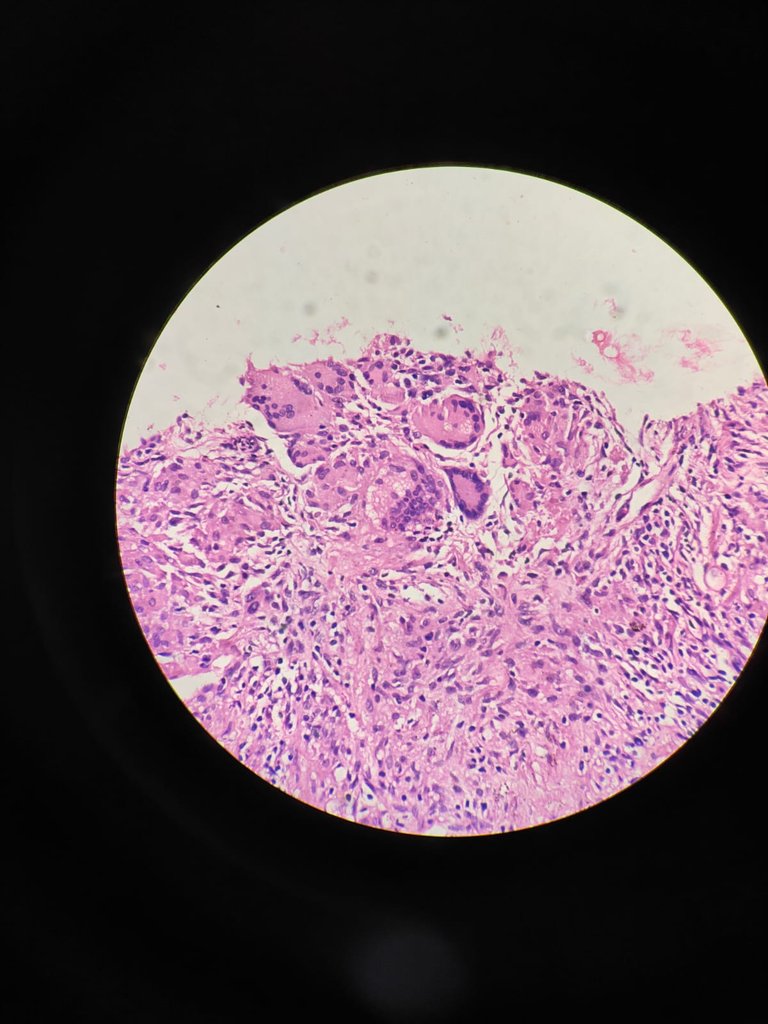
At 40X you have close look up at giant cells, epitheliod cells and lymphocytes.
40X magnification
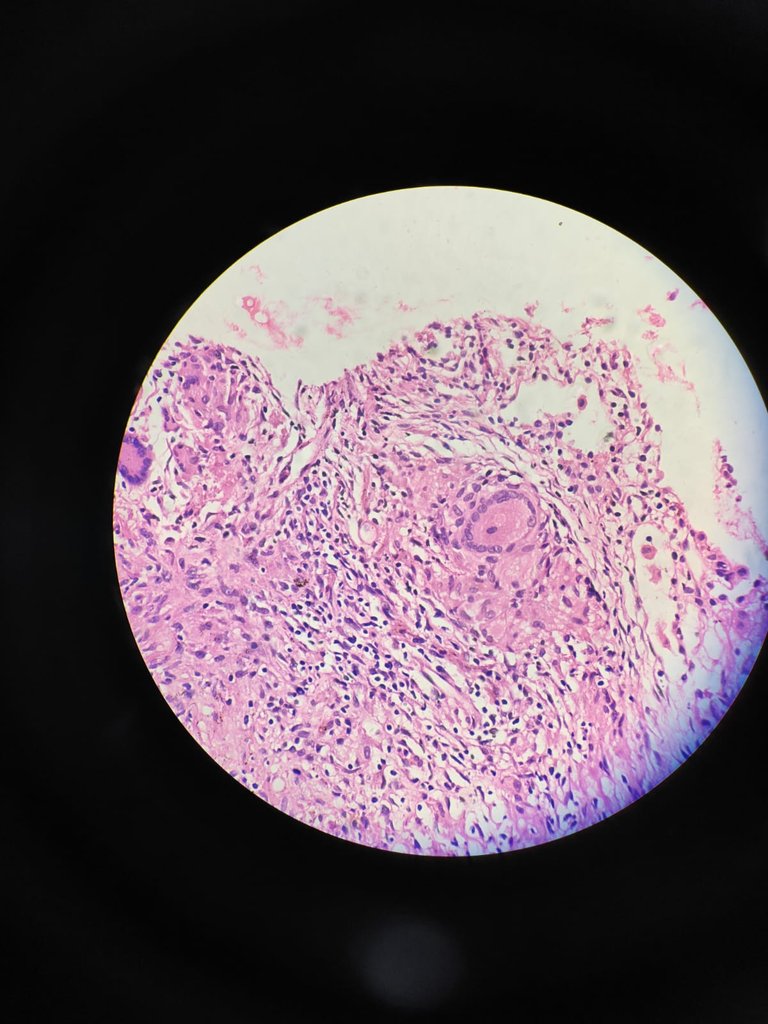
So for confirmation we do ZN stain for Acid fast bacilli (AFB). If we find AFB in the slide then we can vome to conclusion that it is Tuberculosis and the clinician will start ATT.
So this is how we will approach for a TB of Lung.
Thanks for reading.
With regards,
Yours simeon
References
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 10th edition

