It's all about women this week. lol, calm down. The week is tagged breast cancer awareness week by the World Health Organization and also, and today is celebrated as Girl Child's Day. So women are celebrated all over the globe. It's not so deep, yeah but it's dope (it just came, trust me).
Every day a woman is celebrated, there is also a man to celebrate, be it a father, brother, uncle, or husband.
Just to add.
Behind every successful woman, is a selfless man.
So on this note, I welcome you to the midwifery series where we discuss matters about women and their babies. It feels so good that this series coincides with “Women's week”.
Previously in the midwifery series, we talked about the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system and its relevance in pregnancy. We also emphasized the need to have a good understanding of the female reproductive system. Part 1 Midwifery Series
By Heikenwaelder - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
In midwifery, parturition is referred to as the successful passage of the fetus (with the aid of uterine contraction and effort from the mother) through the PELVIS. We casually refer to the fetus as the passenger, the contraction of the uterus as the power, and the pelvis as the passage.
The passage is our focus for today.
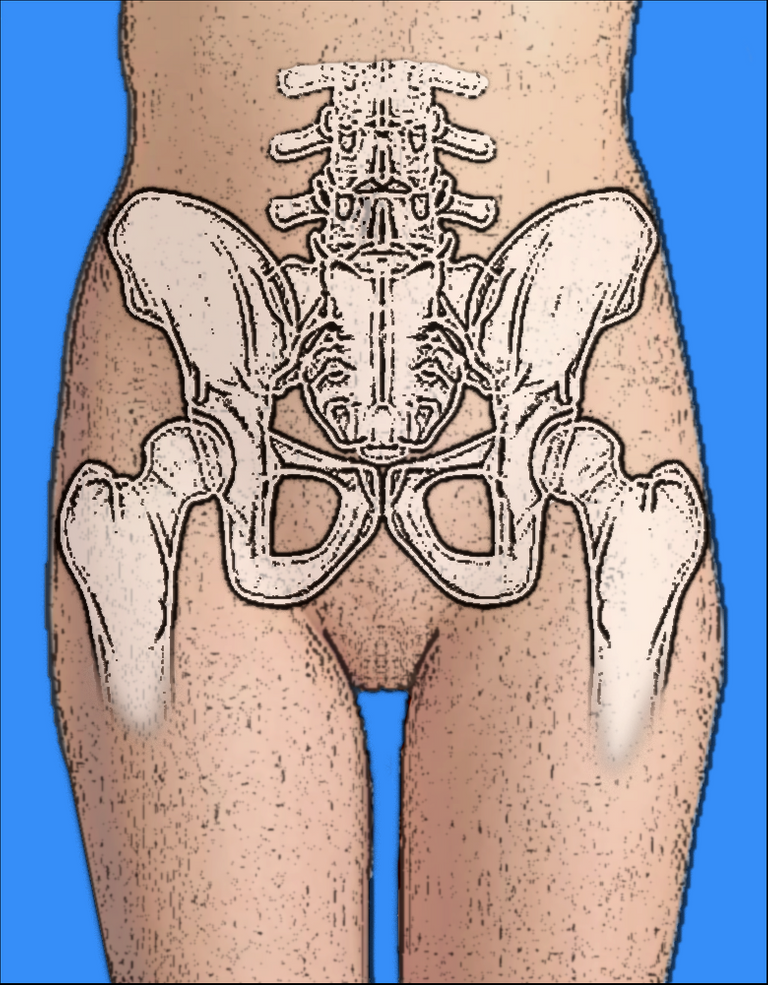
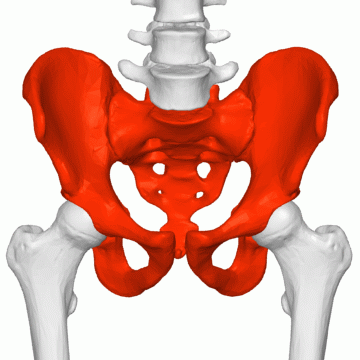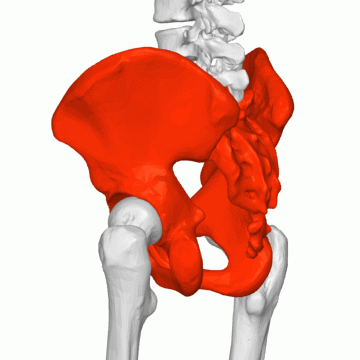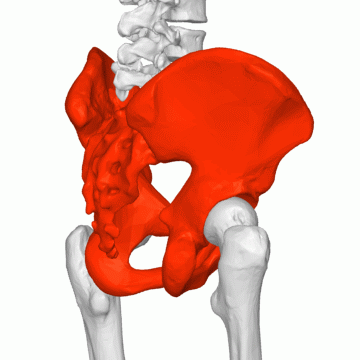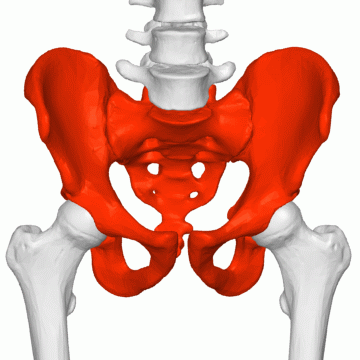
FEMALE PELVIS
By BodyParts3D is made by DBCLS - Polygondata is from BodyParts3D, CC BY-SA 2.1 jp, Wikimedia
The pelvis represents the point of intersection between the abdominal region and the pelvic region. it forms a ring (bony in structure) that transmits the weight of the body to the lower extremities. The pelvis can be imagined as a space with an inlet, walls, and an outlet. The pelvis is composed of 4 bones; the sacrum, the coccyx, and two hip bones. There are 4 major functions of the pelvis in a pregnant uterus Read more on the uterus; it provides support to the uterus, it provides attachment to muscles and membranes to the pelvic floor and permits the passage of the fetus.
The pelvis is formed by the fusion of 3 bones; the ileum, the ischium, and the pubic bone. The pelvis comprises two sections; The false and true pelvis. These sections are divided by the pubic brim. The false pelvis is superior to the pelvic brim. It functions to support the pregnant uterus and also direct the part of the fetus presenting downwards to the true pelvis. The true pelvis is found below the pelvic brim. It is called “True” because it truly plays a vital role in childbearing. Depending on the size and structure of a true pelvis, it functions to direct the presenting part of the fetus downwards to the vagina. The true pelvis must be large enough to deliver a fetus through the vagina. The fetal head normally enters the pelvis in a transverse position and due to the effect of hormones such as relaxin, the pelvis joints relax to enable movement of the fetus around the pelvis. The presence of this hormone may also increase the wideness of the pelvic inlet to aid fetal movement. The pregnant woman might feel this wideness (medically termed ligamental laxity) as pain; which increases due to the weight of the baby and the rotational force, especially when turning in bed.
Exactly why pregnant women should lie on their side first before gently coming out of bed.
The lower portion of the true pelvis is the pelvic outlet. PS: The fetal head must rotate by 90 degrees into the pelvis outlet to be delivered through the vagina.
During labor, the pelvic floor (which houses the pelvis), supports the fetal head while the cervix dilates to allow the passage of the fetus to the vagina.
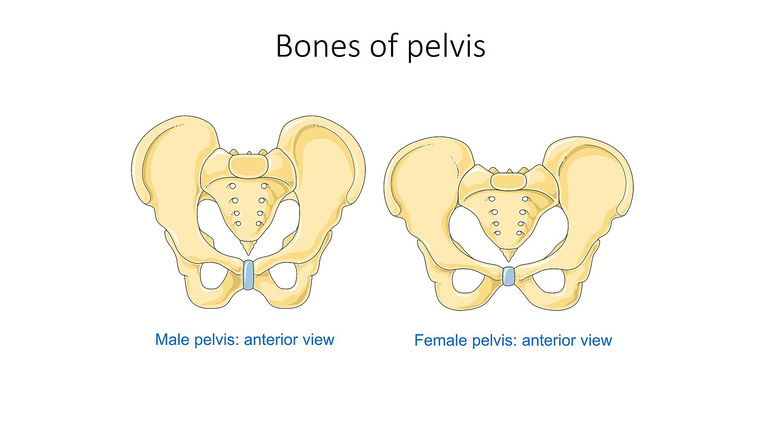
By Laboratoires Servier - Smart Servier website: Images related to Bones of pelvis, Skeleton and bones and Bones --Wikimedia
Generally, the female pelvis is wider and more open than the male pelvis.
There are 4 types of pelvis based on the shape of the pelvic inlet.
Pelvic inlet is the beginning of the birth canal.
Gynecoid Pelvis
Here, the shape of the pelvic inlet is round, shallow, and open. It is the most common type of pelvis in females.
Android Pelvis
Here, the pelvic inlet is shaped like a heart, it is narrower than the gynecoid pelvis.
Anthropoid pelvis
Here, the pelvic inlet is shaped like an egg in an upright position. It is deeper than the Android pelvis.
Platypelliod
Here, the pelvic inlet is flat and wide but shallow. It can be imagined as an egg lying on its side. It is the rarest type of pelvis.
Effect Of This Pelvis On Delivery
Gynecoid Pelvis
Since the gynaecoid pelvis is round, shallow, and open. It gives the fetus room for easy passage hence it is considered the most favorable for vaginal birth.
Android Pelvis
Due to the narrow pelvic inlet, the fetus might move slowly through the pelvis thereby prolonging labor. This type of pelvis favors the Posterior Fetal Position and increases the incidence of forceps delivery.
Anthropoid Pelvis
Women with this type of pelvis may experience long-lasting labor because the passage of the fetus through the inlet might be difficult. Though women with this type of pelvis can still deliver through the vagina in most cases, are referred for a Cesarean Section.
Platypelloid pelvis
This type of pelvis is not conducive for vaginal delivery. It is the widest of all pelvis but its flatness makes it difficult for vaginal delivery hence women with this type of pelvis are delivered through the Ceseaeen section.
How Can I Know My Pelvis Type?
Unfortunately, no test can be done to determine your pelvis type. However, a trained gynecologist, obstetrician, or midwife can help identify your type of pelvis through a procedure called Pelvimetry.
Pelvimetry is a procedure used to measure the female pelvis.
It is done to predict if a woman can be able to give birth through the vagina or not. It can be done clinically or through Computer Tomography Scan, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or X-ray.
Changes In The Pelvis During Pregnancy.
As pregnancy progresses, the pelvis tilts forward to balance the weight of the upper part of the body (including the baby) and the lower extremities. However, this places the woman at risk of lower back pain and also around the pelvic area. There is also increased elasticity of the joints around the pelvis which further increases pain around the pelvis.
Tilting forward of the pelvis accompanied by the increasing weight of the baby places pressure on the bladder (which sits on the pelvic floor) and this leads to stress urinary incontinence usually seen in pregnant women.
Some Tips To Manage Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy.
- Wear supportive shoes (Flat shoes are more recommended).
- Warm water bath to massage the pelvic region.
- Pelvic supportive equipment such as crutches can be used to exercise minimally.
- Lie on the side first before gently leaving the bed.
- Avoid lying on your back.
- Pain relief can be taken (meet your doctor for a suitable prescription).
- Rest when you can.
In summary, Women's bodies differ including the pelvis; which plays a major role in vagina delivery. Pelvis shape does not affect fertility in any way. However, the pelvis type plus the size of the baby plus the position of the baby, and the mother’s efforts are all vital in childbirth through the vagina.
I hope this was beneficial to you.
Do well to drop your thoughts, questions, or additions in the comment section.
Thank you

Image was created by me using Canva.
For Further Reading and References
Anatomy of the Female Pelvis
Type of Pelvis
Effect of different types of Pelvis in delivery
How can I know my pelvis type?
Changes in the pelvis during Pregnancy
Some tips to manage pelvic pain during pregnancy

