
First of all, the most important thing is the cardiac arrest car,
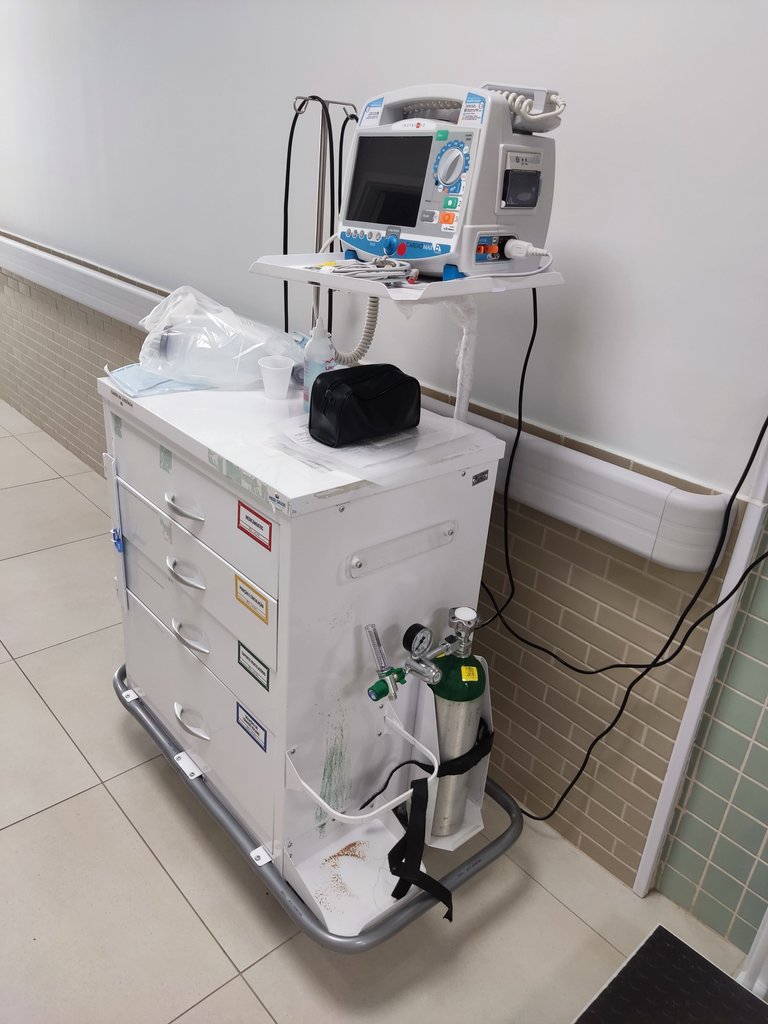
which includes a heart rate monitor, defibrillator, oxygen and manual ventilation resuscitator, and everything else necessary to save lives.
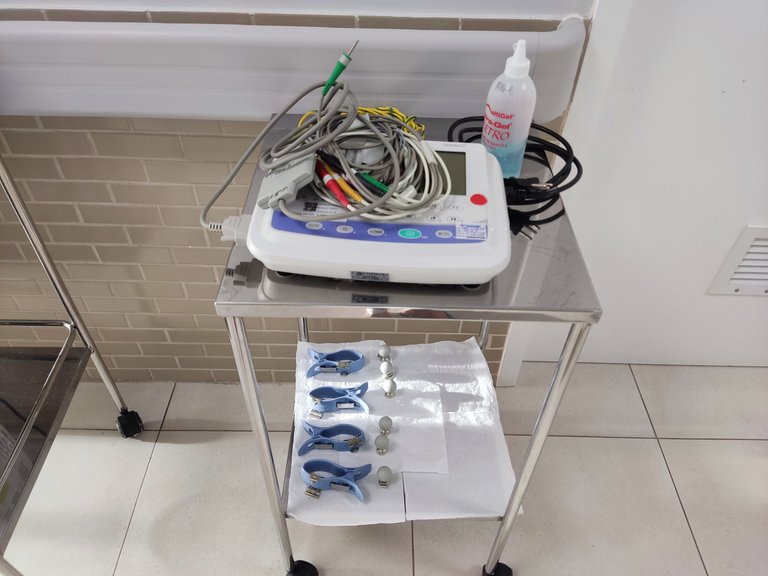

Second is the portable electrocardiogram equipment, to carry out exams without the need for the patient to travel.
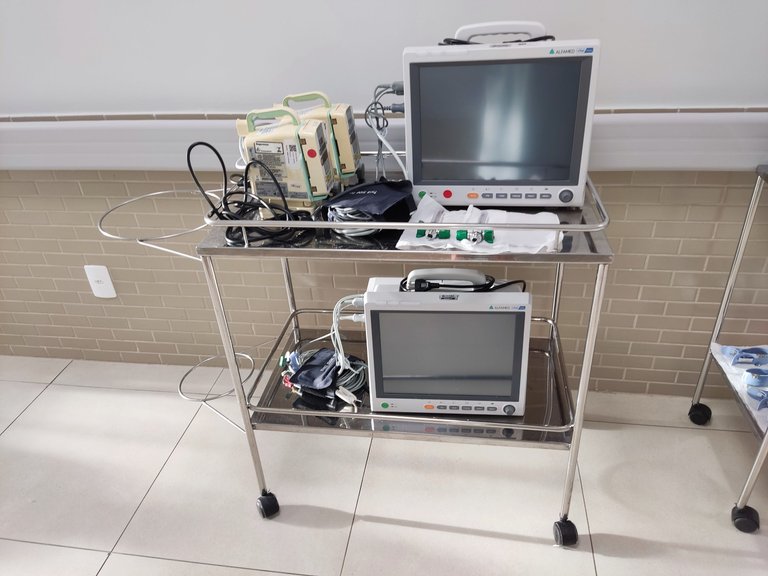

Third is the multi-parameter hemodynamic monitor that allows an analysis of the main vital signs of patients in hospital beds. It monitors heart rate, blood pressure and electrocardiogram. From the data obtained with it, it is possible to draw an overview of the patient's general condition.
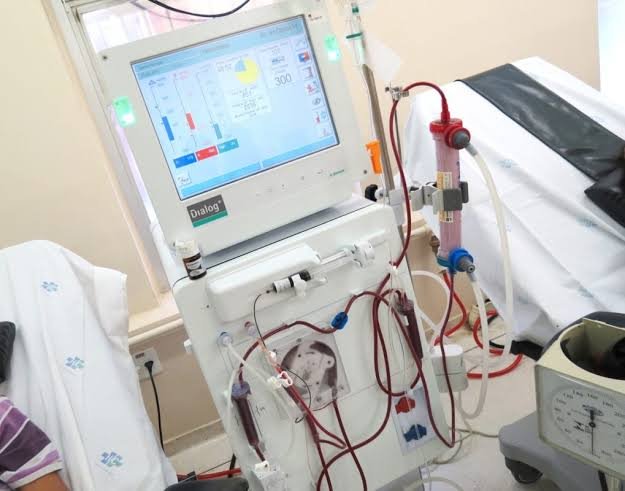
Fourth is the hemodialysis device intended for patients with renal insufficiency, which is connected to a machine that draws their blood through a circulating pump. This blood passes through a filter that has a semi-permeable membrane that removes toxins and excess substances and returns clean blood to the patient.
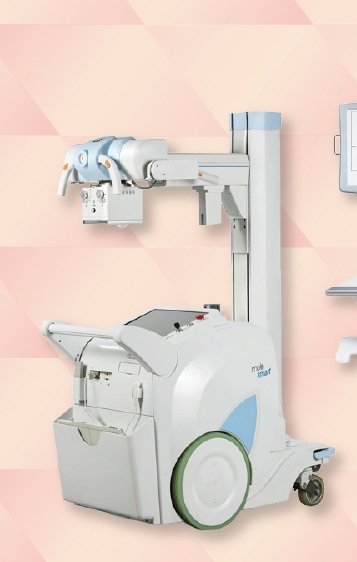
Fifth is the portable x-ray machine The X-ray examination is a quick, simple and painless procedure. To do so, the patient must position the part of the body to be examined on specific equipment, which can be fixed or mobile and is operated by a radiology technician. When he activates a generator, the device emits ionizing radiation – particles that pass through the patient's body and are absorbed by anatomical structures. They reflect on a plate that is placed under the patient and whose material is sensitive to radiation. This is what guarantees the recording of images. The final image presents different colors (shades of gray, black and white), which reflect the degree of difficulty with which the rays pass through the body. This happens because radiation arrives in different forms and intensity in the different tissues that make up the body. Those that are denser, such as bones, for example, are those that absorb the greatest amount of radiation, generating clearer images. On the other hand, softer tissues, such as organs, appear darker.
Segundo é o equipamento de eletrocardiograma portátil, para efetuar exames sem a necessidade do paciente se deslocar.
Terceiro é o monitor de hemodinâmica multi parâmetros que permite uma análise feita dos principais sinais vitais dos pacientes que se encontram em leitos de hospitais. Ele faz o monitoramento da frequência cardíaca, pressão arterial e eletrocardiograma. A partir dos dados obtidos com ele, é possível traçar um panorama da condição geral em que o paciente se encontra.
Quarto é o aparelho de hemodiálise destinado ao paciente insuficiente renal que é ligado à uma máquina que puxa seu sangue através de uma bomba circuladora. Esse sangue passa por um filtro que possui uma membrana semipermeável que retira as toxinas e as substâncias em excesso e devolve o sangue limpo para o paciente.
Quinto é o aparelho de raio-x portatil
O exame de raios X é um procedimento rápido, simples e indolor. Para fazê-lo, o paciente deve posicionar a parte do corpo a ser examinada em um equipamento específico, que pode ser fixo ou móvel e é operado por um técnico em radiologia.
Quando ele aciona um gerador, o aparelho emite uma radiação ionizante – partículas que atravessam o corpo do paciente e são absorvidas pelas estruturas anatômicas. Elas refletem em uma chapa que é colocada sob o paciente e cujo material é sensível à radiação. É o que garante o registro das imagens.
A imagem final apresenta diferentes cores (tons de cinza, preto e branco), que refletem o grau de dificuldade com que os raios atravessam o corpo. Isso acontece porque a radiação chega de diferentes formas e intensidade nos diversos tecidos que compõem o corpo. Aqueles mais densos, como os ossos, por exemplo, são os que absorvem a maior quantidade de radiação, gerando imagens mais claras. Por outro lado, os tecidos mais moles, como os órgãos, aparecem num tom mais escuro.
 ) Gif by [@aleister](https://steemit.com/@aleister)
All photos by @pataty69
) Gif by [@aleister](https://steemit.com/@aleister)
All photos by @pataty69


Gif by @doze

