When soil becomes saturated with rainfall, all the pores between the soil particles are filled with water and there's no room for air. Soil microorganisms(denitrifying bacterias) are unable to breathe due to lack of oxygen so instead, they reduced soil nitrate (NO3-) and nitrite (NO2-) to a gaseous form of nitrous oxide (N2O), nitric oxide (NO), and nitrogen gas(N2) a process called denitrification.
Denitrification is the process by which nitrogen atoms of nitrate and nitrite are returned to the atmosphere as nitrous oxide and nitrogen gas. This Nitrogen gas is conserved and recycled back into the soil during Nitrification.
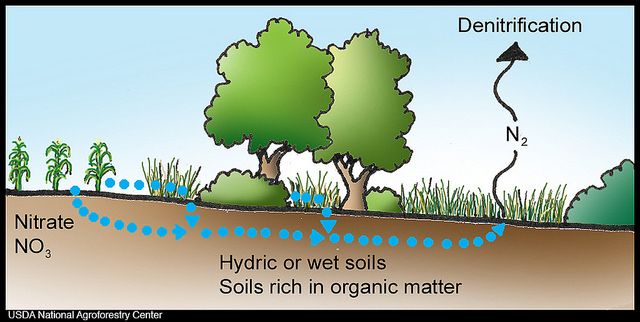
Denitrification is an anaerobic respiration process performed by denitrifying bacteria. Most denitrifying bacteria are facultative anaerobic bacteria i.e, they can survive in both presence or absence of oxygen. Examples are Thiobacillus Denitrificans, Achrombacter, and Pseudomonas.
The image above is an example of a microorganism called ACHROMBACTER.
 An image example of PSEUDOMONAS image source
An image example of PSEUDOMONAS image source
An image example of THIOBACILLUS DENTRIFICANS Source
The process of denitrification is a way in which nitrogen is lost in the soil. when nitrogen is lost it depletes soil fertility and reduces agricultural productivity. Nitrogen is essential for the growth of plants and it's a constituent of many biomolecules which dependent on life. Denitrification leaks nitrous oxide (N2O) which is an Ozone-depleting substance and a greenhouse gas that can have a considerable influence on global warming. Nitrous oxide is more effective in the absorption of atmospheric infrared radiation than carbon dioxide causing ozone depletion and death to life in the ecosystem.
1)The soil microorganisms
2)The oxygen supply in the soil.
a)soil PH (measure the acidity and alkalinity)
b) soil water content
c) soil nitrate
d)soil oxygen supply
e)the amount of organic matter
f) soil temperature.
These factors are dependent on the two main factors above. ie. anything that affects these two factors will have a greater effect on the two major factors and the degree of nitrogen lost.
SOIL WATER CONTENT: - Denitrification becomes critical when the soil is waterlogged for a day and a half or more. The longer the soil is waterlogged, the more the loss of nitrogen in the soil. In this case of waterlogging, nitrate move below the root zone of plants and down into groundwater causing root anoxia and increasing the potential for denitrification because this microorganism lacks oxygen supply due to the accumulation of nitrate into groundwater.
SOIL TEMPERATURE - Because the process is biological, and microbes tend to move faster at a higher temperature, they need more oxygen supply and thus tend to convert more nitrate and nitrite to gaseous nitrogen which increases the denitrification process. The optimum temperature for denitrification is about 140 degrees Fahrenheit.
SOIL PH - soil pH measures the acidity and alkalinity of the soil. Denitrification in acidic soil is very low compared to slightly alkaline soil. The optimum soil pH for the production of Nitrogen gas and Nitrate is 6.6 - 8.3.
Soil oxygen supply - Oxygen is one of the most factors of denitrification. it is considered to be inhibitory for identifying bacterias.. increase in Oxygen supply decreases the potential for denitrification.
Denitrification of biogeochemical is a naturally occurring process in the ecosystem. It occurs with or without the invasion of man. it helps to conserve the energy flow as well as the organic molecules on the earth. Some of the organic molecules when returned to the atmosphere in their oxide form cause an effect on the Ozone layer. To minimize these factors that influence denitrification are studies for a better understanding of crop nutrition and how to save Ozone depletion.