Greetings, friends of Hive

For March, the Med-Hive community has chosen as a theme Women's health, I invite you to join the participation, here is the link.
In the first installment, we present information about the female internal genitals, their structure, and functioning. If you are interested in reading it, you can access from here.
In this publication, we will learn or refresh our knowledge about the anatomy of the external genitalia, by this I mean how they are structured, what they do, and how they function. Join me on this journey, let's do it together.
Female external genitalia
The vulva
It is a collective term used to include all the structures that are part of the external female genitalia. The structures that make up the vulva are: mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoral hood, clitoris, vulva vestibule and hymen.
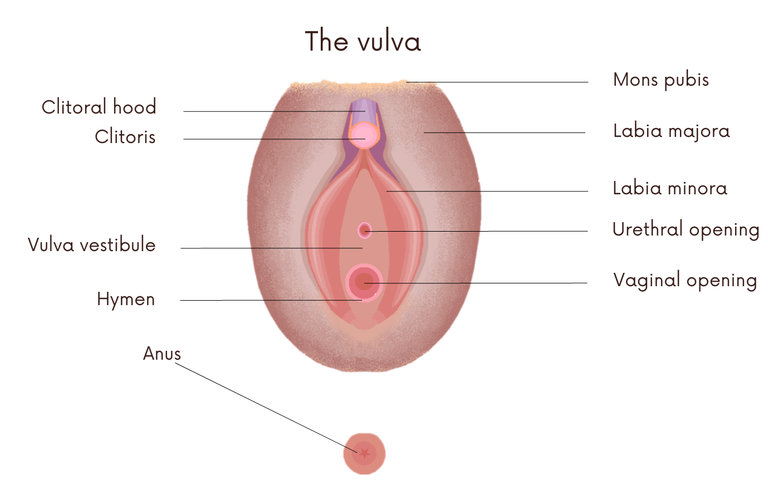 External anatomy.
External anatomy.Credit: Sciencia58 CC0 1.0 license Universal Public Domain.Edited in canva
The function of these organs is to protect the internal organs from infections and to favor the entrance of spermatozoa into the vagina.
Mons pubis
It is a rounded pad of fatty tissue, which sits on the pubic bone. It is prominent and usually from puberty onwards it is covered with triangular shaped hair (pubic hair). Its purpose is protection during sexual intercourse. It is worth mentioning that this area has sebaceous glands that release pheromones to induce sexual attraction.
Labia majora
They are a pair of skin folds, named because they are the largest labia. They cover and protect the labia minora, the clitoris, the vestibule of the vulva, and the urethral and vaginal opening. During sexual arousal (desire, enthusiasm) they fill with blood and increase in size.
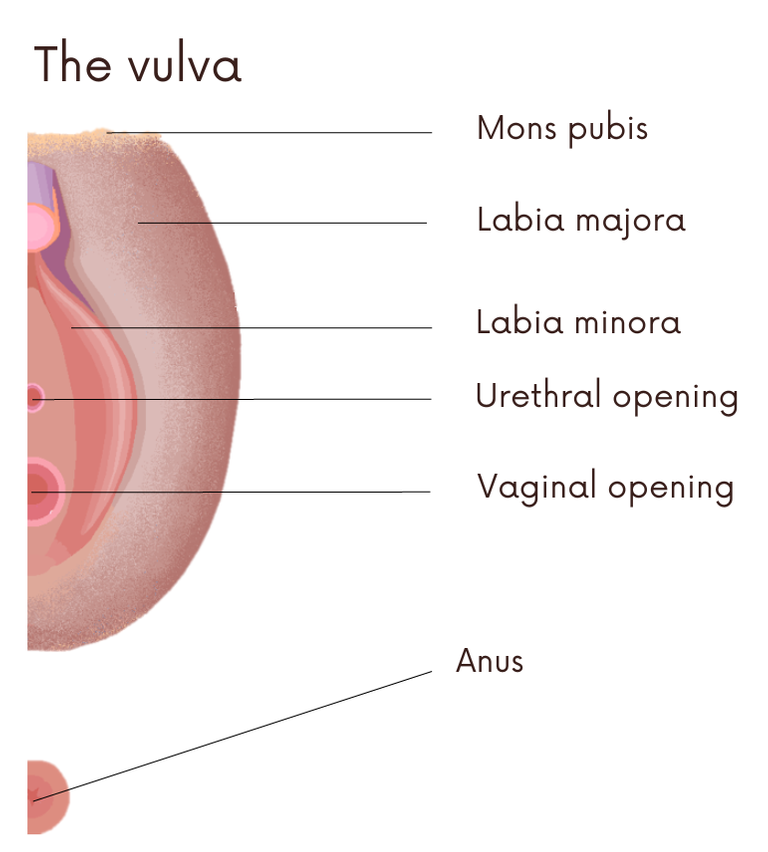 External anatomy.
External anatomy.Credit: Sciencia58 CC0 1.0 license Universal Public Domain.Edited in canva
Labia minora
They are the smallest labia, also a pair of folds of skin, parallel to the labia majora and surround the entrance of the vagina. In the same way as the labia majora, when sexual arousal occurs, they fill with blood and increase in size.
Clitoral hood
It is a small tissue that protects the external part of the clitoris and is highly sensitive. It is located on the upper part of the clitoris.
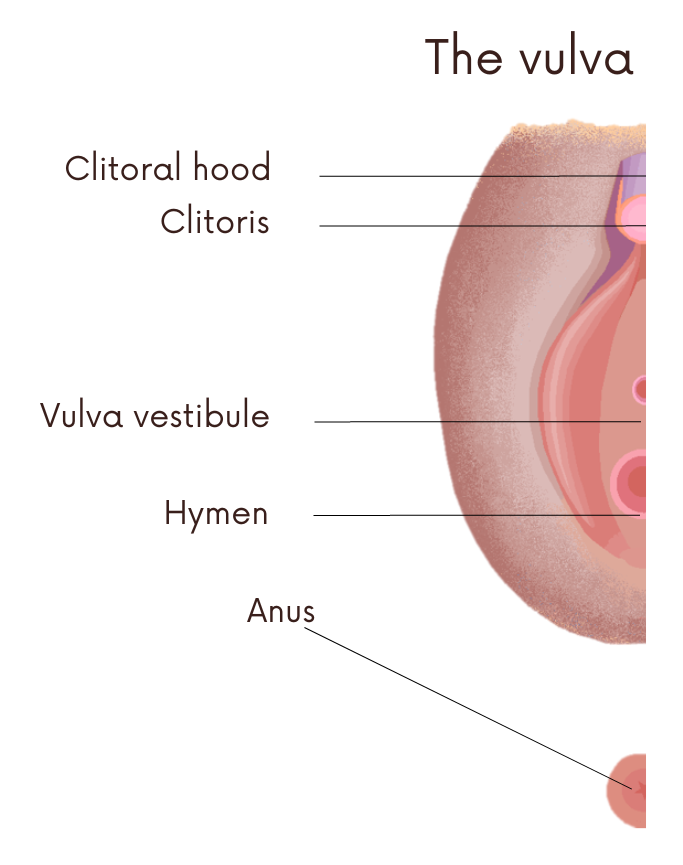
External anatomy.
Credit: Sciencia58 CC0 1.0 license Universal Public Domain.Edited in canva
Clitoris
It is a protuberance of spongy tissue, formed by thousands of nerve endings and many blood vessels (it is the homologous to the glans penis in men). It is a sexual and sensory organ, responds to sexual stimulation, with arousal (desire, enthusiasm) increases its size and is responsible as the main organ of female orgasms (point of greatest satisfaction).
Vulva vestibule
It is an area where the opening of the urethra and the entrance to the vagina are located. It has a smooth surface. Here there are glands that produce fluid to keep the area moist and lubricated. During sexual arousal they increase the production of fluid to further promote lubrication.
Hymen
It is a thin, fragile membrane that covers part of the vaginal orifice. Although its rupture is associated with the first intercourse, ruptures associated with physical activities have been described. Also, there will not always be bleeding and pain after rupture.
There are different shapes and sizes, such as the extreme imperforate hymen (covering the entire vagina), which causes obstruction and requires a surgical procedure for its correction. Hymen agenesis (absence of hymen from birth).
Some considerations
Ladies, to take care of your body and be healthy, you have to discover it, understand it, know your organs, what you live and experience with them. By understanding how they work, you will perceive in time, even if you do not know the real cause, that something is happening that is not "normal" or that things are not going well. Alarm bells will ring and you will immediately seek specialized help, from your trusted doctor or a health center..
Be consistent in your visits to your health specialist, do not neglect.
Gentlemen should know the female body, its structures and functions, especially those associated with the gynecological area. It is the integral conception of health. By taking care of your ladie, your partner, your wife; you are also taking care of yourself. In the same way, ladies should familiarize themselves with the male genital organs. Thus, the care will be integral and reciprocal, generating positive expectations for both for a full physical, mental and sexual life.
The vast majority or perhaps the most frequent diseases of the gynecological sphere should be managed and treated as a couple to solve and restore the health of both men and women.
I always insist on self-care, but today let us broaden the horizon in our vision of health, let us look at the field of collective health, self-care is also exercised when I take care of my partner, my children, my family and my community. Because these are attitudes and/or habits that contribute to preserve our health.

Credit: Ben White Public domain
Thus we conclude this second installment of the female anatomy. Next time our topic will be the breasts or mammary glands.
Bibliographic references consulted
-Biggers A. Female reproductive organ anatomy. [Internet]. 2021 [quoted 2023 March] Available at
-Cleveland Clinic. Female reproductive system. [Internet]. 2022. [quoted 2023 March] Available at
-Johnson T. Your guide to the female reproductive system. [Internet]. 2022. [quoted 2023 March] Available at
-Nguyen J., Duong H. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, female external genitalia. [Internet]. 2022. [quoted 2023 March] Available at





