By Scientific Annimations, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
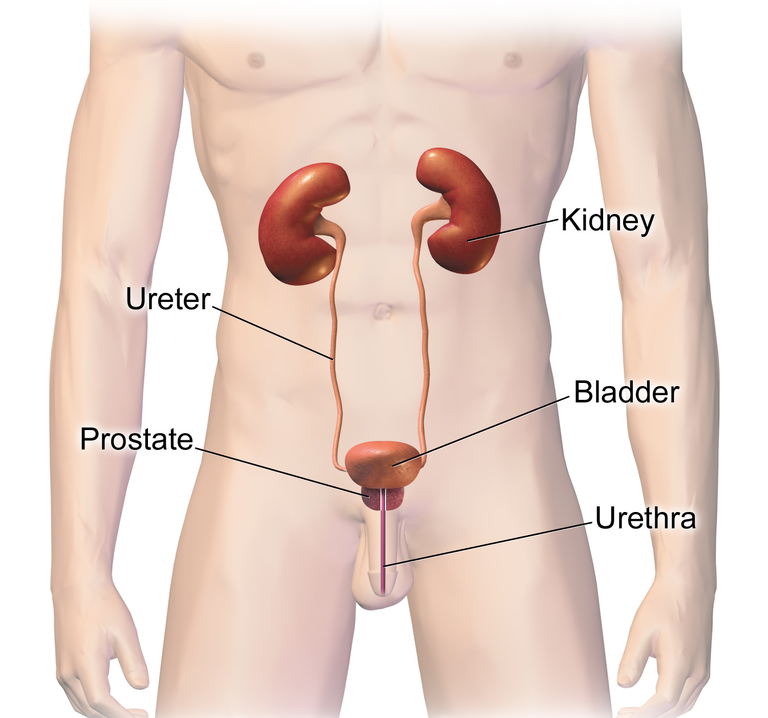
The bladder is an organ in the body that stores urine. The urine is produced in the kidneys, it is then transported to the bladder through the ureters. In the bladder, the urine is stored temporarily before it is then voided through the urethra.
However, in some conditions, there can be an obstruction to the bladder outlet through which the urine is voided. The commonest obstruction occurs at the urethra which is a pipe that connects the bladder to the exterior.
This obstruction causes the retention of urine in the bladder and can occur suddenly which is referred to as acute urinary retention or it can occur over time which is referred to as chronic urinary retention.
Acute urinary retention can be a very traumatic experience. We all know how disturbing it can be when you are pressed. Now imagine having a full bladder for days and no point of exit to empty the bladder. Most times when they present to the hospital, they come very restless, agitated, febrile, and all that. But the passage of a urinary catheter can be reliving and works like magic.
SYMPTOMS OF BLADDER OUTFLOW OBSTRUCTION
For those who have Chronic urinary retention, the bladder outlet is narrow but not totally blocked. So they can still pass a small quantity of urine, but still have more than the normal quantity of urine retained in the bladder. The normal volume of urine retained after passing urine is about 50ml. However, for those who have chronic urinary retention, the residual volume is over 250ml.
Because of this large volume retained in the bladder after voiding, they have symptoms that can be grouped as Irritative and Obstructive symptoms.
The irritative symptoms occur because the large volume of urine left in the bladder irritates the bladder. So the person will start having increased frequency of urination. Here, the bladder is trying to push out the excess residual volume but it's not going out due to the obstruction. So the person visits the restroom now and then to pass only a small volume of urine, yet feels pressed.
Another irritative symptom is urgency and urge incontinence. Here, the person cannot hold urine for a long time. The moment he feels pressed, he must rush to the restroom immediately. This is because the bladder is irritated by more than normal residual volume of urine. There can also be nocturia.
By BruceBlaus - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
Obstructive symptoms are symptoms that occur due to the blockage of the bladder outlet. So the person experiences straining while passing urine. This is because he is trying to apply pressure to overcome the resistance at the outflow tract. Due to this obstruction, he is also having a weak stream of urine. There is also intermittency, the urine flows, stops, flows again, stops, and so on.
Another obstructive symptom is incomplete voiding. No matter how he pushes, he still feels some urine left in the bladder. There are also terminal dribbling, hesitancy, and overflow incontinence. When there is a coexisting urinary tract infection, there may be painful urination. There may also be associated blood in the urine (haematuria).
COMPLICATIONS OF URINARY RETENTION
Due to the retention and stasis of urine in the bladder, the urine becomes a culture medium for microorganisms which predisposes the individual to urinary tract infections. The stasis of urine in the bladder also leads to the formation of bladder stones.
As the urine keeps building up without exiting, at a point, it starts to flow back to the kidneys in a condition called hydroureter and hydronephrosis. When this process continues, the kidneys get drowned in their urine, and kidney failure results.
Other complications include poor quality of life, sleep disturbance, erectile dysfunction, haematuria, etc.
CAUSES OF BLADDER OUTFLOW OBSTRUCTION
There are many causes of bladder outflow obstruction but the commonest ones are Benign Prostatic Enlargement, Prostrate Cancer, Urethral Stricture, and Meatal Stenosis. We will discuss each cause briefly.
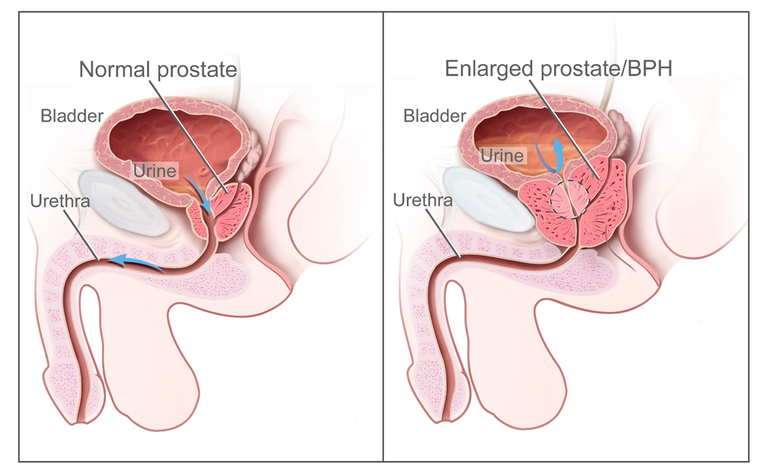
BENIGN PROSTATIC ENLARGEMENT
The prostate gland is a gland found below the neck of the bladder. It is found in men and secretes fluid that makes up part of the semen. The gland surrounds the upper part of the urethra and any enlargement of the gland presses on the urethra and narrows it. This results in bladder outflow obstruction and commonly occurs with advancing age in men.
By National Cancer Institute, AV Number: CDR462221, Public Domain, Wikimedia
Treatment of Benign Prostatic Enlargement also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) depends on the international prostrate scoring system. The available options are Watchful waiting or active surveillance, and medical therapy like Doxazosin, Tamsulosin, Finasteride, etc.
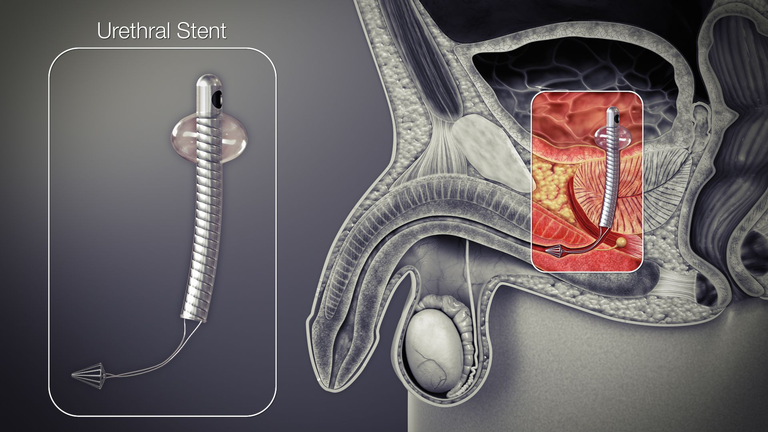
There are also options for minimally invasive procedures like High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound, Intra urethral stents, Transurethral vaporization of the prostate, etc. There is also an option for surgery like Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
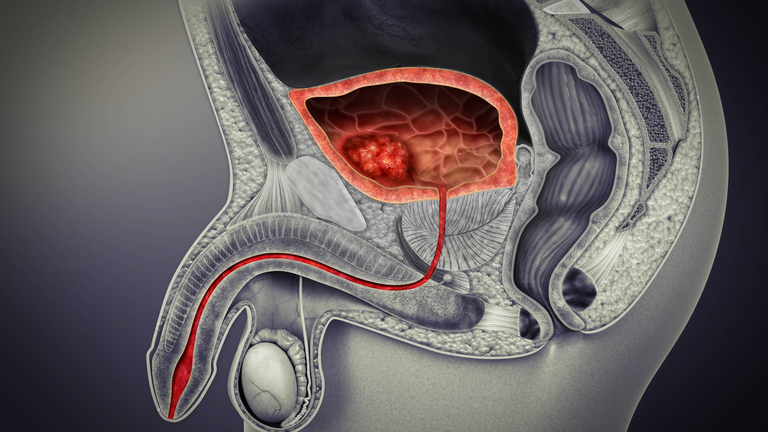
PROSTATE CANCER
This is an abnormal uncontrollable growth of the prostate gland. This causes the prostate to enlarge and press on the urethra thereby causing bladder outflow obstruction.
The available treatment depends on the stage and can be watchful waiting, surgical removal of the prostate gland, or the use of radiotherapy. Hormone therapy and anti-androgens can also be used.
URETHRAL STRICTURE
This occurs when there is an occlusion of the lumen of the urethra (the pipe that connects the bladder to the exterior). This occlusion can be caused by a previous inflammation of the urethra following a urinary tract infection. It can also be from a trauma to the urethra or a previous passage of urethral catheter or Endoscopic procedures.
The treatment can be serial dilatation, surgical removal of the stricture in a process called Visual Internal Urethrotomy (VIU), or a repair of the urethra in a process called Urethroplasty.
By Scientific Annimations, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
Other causes of bladder outflow obstruction include bladder stones, bladder neck problems like stenosis, bladder cancer, neurogenic bladder, etc.
In children, the commonest causes include Posterior Urethral valve in males. For females, there is urethral atresia.
CONCLUSION
There are many causes of bladder outflow obstruction. The early stage presents with the irritative and obstructive symptoms described above. It is always important to see a doctor at an early stage.
When not addressed early, it can lead to complications and progressive kidney failure. Therefore, those who notice any of the above symptoms should see a doctor immediately for proper evaluation and treatment. Further delay may result in life-threatening complications.
Thanks for reading.
For references and further reading, please visit;
