By Myupchar, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
Chronic liver disease is a progressive spectrum of disease that moves from reversible to irreversible stages. Therefore it means that when caught at an early stage, the progression can be stopped. Once it progresses to advanced stages, a liver transplant will be the only option.
So, in this post, I will give an overview of what chronic liver disease is, the common causes amongst us, the early signs and symptoms, the treatment, and then prevention. This is very important because the early signs and symptoms may be unspecific, but I will point out some key features of chronic liver disease at various stages.
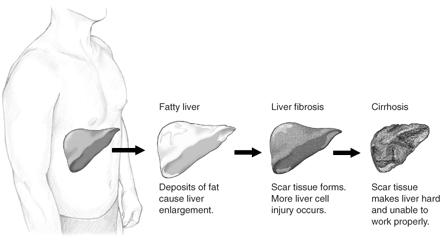
Liver disease is said to be chronic when it has lasted for more than 6 months. It normally moves from inflammatory processes in the liver, to fibrosis and then to cirrhosis which is the replacement of the liver cells and tissues with scar tissues. This stage of liver cirrhosis can as well progress to form liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
CAUSES OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
- Alcoholic liver disease.
This is one of the commonest causes of chronic liver disease in our environment and it is found among those who have a high intake of alcohol for a long period. This long-term alcohol intake leads to the accumulation of fat in the liver, an Inflammatory process, and damage to the liver.
This is one of the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol destroys the liver cells and forms scar tissues which replace the normal liver cells thereby leading to the impairment of liver functions.
By Countincr, Public Domain, Wikimedia
- Chronic Viral Hepatitis Infections
There are many types of viral Hepatitis infections which include Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. While Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E cause acute liver infections which usually are self-limiting, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and Hepatitis D cause chronic liver infections which progress to liver failure. Hepatitis D always occurs as a co-infection with Hepatitis B.
- Autoimmune liver diseases.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body develops antibodies to fight its organs and tissues. In this case, the autoantibodies attack the liver tissues and damage them which results in liver failure.
These autoimmune diseases of the liver include; autoimmune Hepatitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Fatty Liver disease
This may be alcoholic fatty liver disease or non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alcoholic fatty liver disease occurs from chronic and excessive intake of alcohol while the non alcoholic fatty liver disease occurs in people who are obese, diabetic, hypertensive, or have excessive body fat (hyperlipidemia).
- Hepatic Vein thrombosis
This occurs when there is a blockage of the blood vessels of the liver.
- Drugs
Certain drugs are toxic to the liver and can lead to chronic liver disease. Some of these drugs include Isoniazid used to treat Tuberculosis, Methotrexate used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, etc, amiodarone used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, phenytoin used to treat seizures, etc.
- Certain inherited diseases like hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, etc.
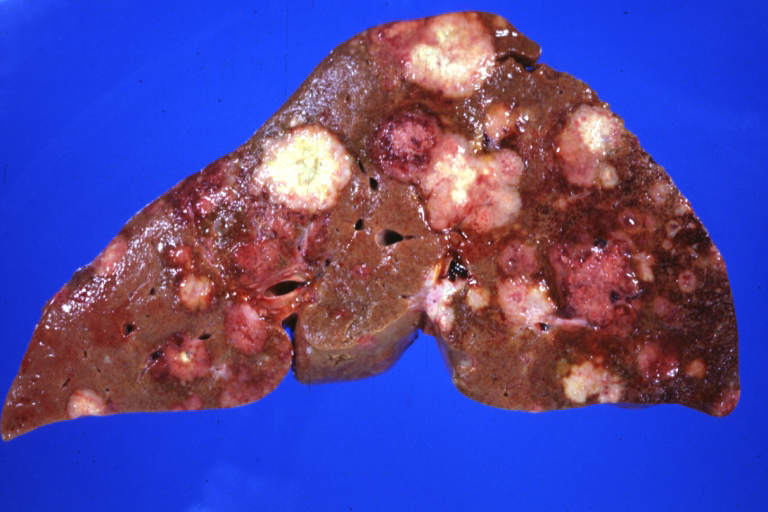
By The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP), Public Domain, Wikimedia
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
The manifestation of chronic liver disease occurs in 2 phases. In the first phase when liver damage is just setting in, the liver tries to readjust and adapt to cope with the damage.
This stage is said to be the compensated stage and the patient may not have any symptoms. When symptoms are present, they usually have a feeling of unwell, weakness, weight loss, joint pain, fever, etc which are non-specific symptoms.
They can also have specific features of compensated liver disease which include; dark spots in the palms, swelling at the sides of the face (parotid swelling), hair loss, white nails, yellow growth around the eyelids (xanthelasma), spider nevi, testicular atrophy, finger clubbing, etc.
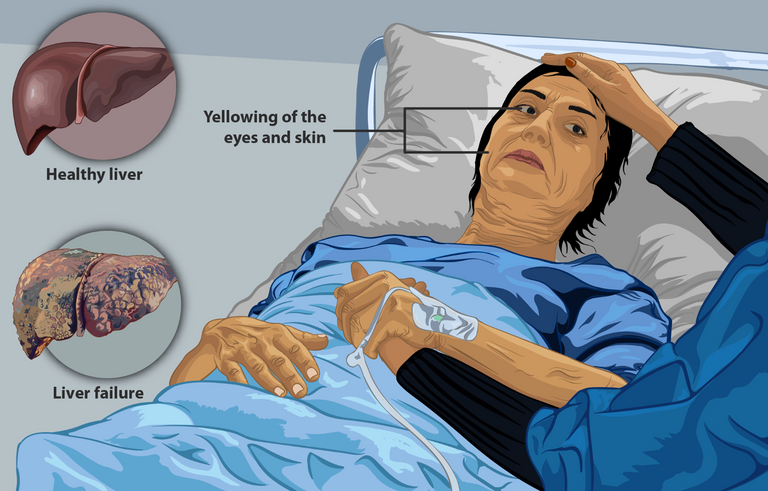
As the liver disease progresses, it will get to a point when the liver can no longer cope with the ongoing damage. This stage is the decompensated phase and presents with more severe features like disorientation, yellowness of the eyes, drowsiness, coma, personality changes, altered sleep pattern, flapping tremors, dilated abdominal veins, abdominal swelling, spleen enlargement, a strong musty smell of breath (fetor hepaticus), portal hypertension, etc.
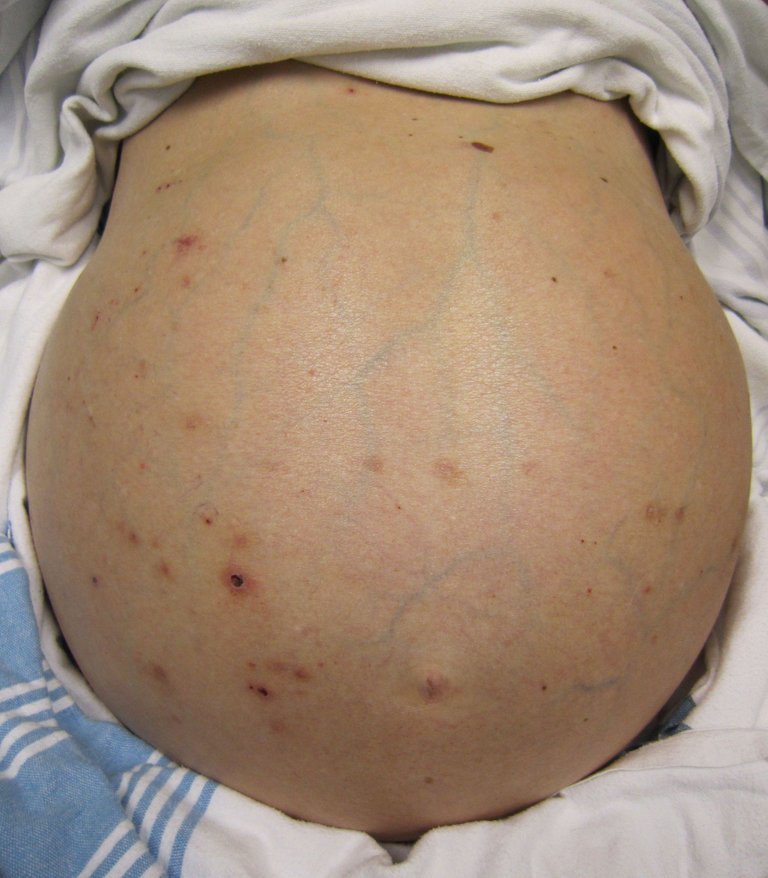
By James Heilman, MD - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
PREVENTION OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
From the causes above, we can see that many things can result in chronic liver disease. This is why the incidence of this disease is very high and many people come down with it. According to the Lancet,
There were an estimated 1·5 billion cases of chronic liver disease worldwide in 2017 including 10·6 million cases of decompensated cirrhosis and 112 million cases of compensated cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis accounted for an estimated 1·32 million deaths in the same year.
This burden, which is probably underestimated, is highly concerning.
This incidence is even higher in developing countries due to Chronic Hepatitis infections, excessive alcohol consumption, drug toxicity, metabolic syndrome, and others.
At the advanced stage of liver disease when liver cirrhosis has occurred, the disease is irreversible and the total cure is only a liver transplant. The cost of liver transplants and the unavailability of donor organs is also big problem. So prevention remains our best bet. How can we prevent this disease?
- Avoid excessive alcohol intake.
Over 90% of the alcohol consumed goes to the liver for detoxification and metabolism. This alcohol as well as the products of their degradation cause serious damage to the liver which progresses to liver failure. Therefore, those who consume large quantities of alcohol should abstain from that.
Heavy alcohol consumption is a health challenge globally and especially in rural communities where we have habitual drunkards. Some of them come down with liver failure from this act and it's usually undiagnosed because they assume that the man was poisoned but it's not any poison, its a liver damage from alcohol. Therefore, alcohol must be taken in moderation.
By Identify, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
- Vaccination against Hepatitis B and Hepatitis A.
Vaccination against Hepatitis B will offer protection against this viral infection which is a notorious cause of chronic liver disease and liver failure.
These viruses can also be gotten from unprotected sexual intercourse, blood transfusion, use of unsterilized needles and sharps, etc. So we must avoid these things.
- Drugs must be taken on prescription.
The use of drugs for the wrong reasons or wrong dosages as well as herbal medications can predispose to liver damage. Therefore, all drugs must be taken as prescribed by the doctor.
Avoid contact with toxic chemicals, insecticides, pesticides, etc. The toxins from these chemicals can damage the liver too.
It is also important to maintain a healthy weight, blood pressure, body fat and regular exercise as obesity, diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia may predispose to fatty liver disease and chronic liver disease.
In conclusion, chronic liver disease is a very common disease. It is progressive and once it has reached the advanced stage, it is not curable except by liver transplant. The causes are many and they are all around us. So we must protect ourselves from them.
Early detection is also very important and the progression of the disease can be halted when noticed early. This early detection can be a challenge because the symptoms that occur at the early stage may not be specific. The patient may not even think of liver disease.
However, in this post, I have been able to list some of the early signs and symptoms as well as the causes of chronic liver disease and most importantly, how we can prevent this disease.
In my next post, I will talk about the problems of chronic liver disease and how they can be managed to enable the patient live a better life even in the absence of a liver transplant.
Thanks so much for reading.
You may check the resources below for more information on chronic liver disease and references.





