These days really have been quite complicated for me in terms of work, to the point that I have not posted for a couple of days, nor have I commented much, something I usually do, but that's life, sometimes things become a little laborious, more than usual. I hope you are doing well, and that you can enjoy this coming weekend.
This time I want to talk to you about a disease that is contracted by eating some plants in particular, and it is usually due to poor hygiene when preparing them. Considering that we all eat, we all deserve to do so for health maintenance reasons, this means that in theory anyone could contract fascioliasis.
Fortunately it is not so common, but the cause of this is similar to other diseases such as amebiasis, therefore, by preventing a disease of this type we would practically be preventing others. So I invite you to read on, what I have to tell you will surely interest you.

Let's first see what this disease is:.
Fascioliasis is a parasitic disease caused by the trematode Fasciola hepatica. This parasite mainly infects livestock, but it can also affect humans who consume plants contaminated by the parasite.
Ok, I know not everyone will know what a trematode is, I define it: it is a flatworm, which particularly have a complex life cycle, which includes the need for multiple hosts to complete their life cycle. This is where the human being comes in, within the hosts that can be infected by the parasite, and serve as a site for its evolution and in the process make humans sick.
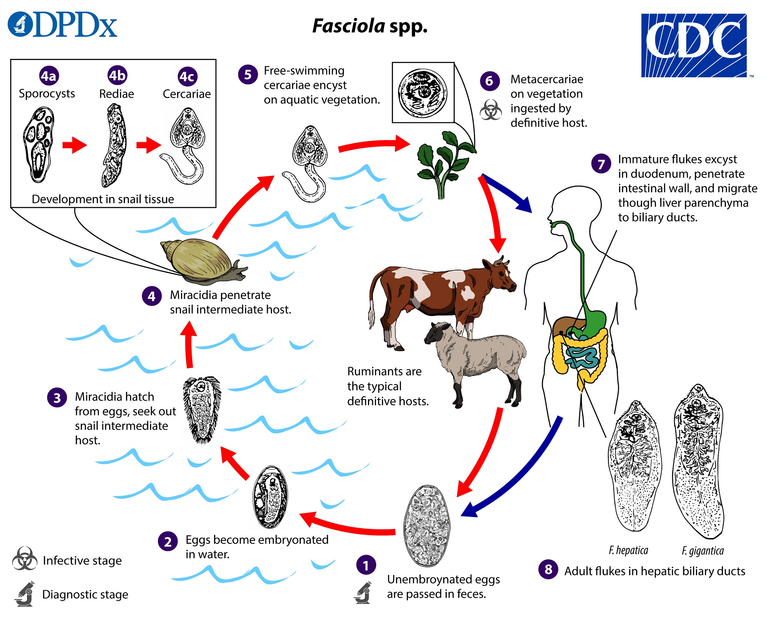
The life cycle of this parasite is particularly complex, as I said before, it requires several hosts for its evolution, let's see it below, you can be guided by the image above to understand it much better:
Eggs: Fasciola hepatica eggs are eliminated in the feces of the final hosts, which are mainly herbivores such as cows, sheep, goats and other similar animals. The eggs are released into the environment and, if conditions are suitable, may hatch and release a larva called miracidium.
Miracidia:
The miracidia larva swims in the water and searches for a snail as an intermediate host. Once it has found a suitable snail, it enters its body through its respiratory surface.Sporocyst: Inside the snail, the miracidia larva transforms into a different larva called a sporocyst. The sporocyst divides and forms multiple smaller sporocysts, which in turn form another type of larva called a cercaria.
Cercariae: are released by the snail into the water and attach themselves to aquatic plants (lettuce, watercress, spinach, etc.). This is the point where, if there is no proper food hygiene, humans can become infected.
Metacercaria: If an herbivorous animal eats a plant containing cercariae, the cercariae can penetrate the animal's tissue and form a structure called a metacercaria. The metacercaria is the infecting form of Fasciola hepatica for the final hosts, including humans.
Adult: The metacercaria is released into the small intestine of the final host and penetrates the liver, where it develops into a full adult. Adults live in the bile ducts of the liver and lay eggs that are released in the feces of the final host, completing the life cycle.
As you can see, it goes through many living things during its life cycle.

Now let's see how Fascioliasis can present itself, what is its symptomatology, which can be confused with many other diseases.
Abdominal pain: Fascioliasis can cause abdominal pain, especially in the upper right part of the abdomen, where the liver is located. Since this is where it fulfills part of its life cycle, causing a rather complex inflammatory reaction.
Fever: Patients with fascioliasis may develop fever, especially in the acute stages of the infection.
Nausea and vomiting: Fasciola hepatica infection may cause nausea and vomiting, especially if there is significant infection in the liver.
Loss of appetite and weight loss: Fascioliasis can cause a loss of appetite and weight loss, especially in chronic cases of infection.
Fatigue: Patients with fascioliasis may experience fatigue and weakness, which may be a symptom of anemia if the infection has affected red blood cell production.
Jaundice: Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes, may be a symptom of advanced fascioliasis if the infection has caused significant liver damage. Or if it also affects the bile ducts.
Muscle and joint pain: fascioliasis can cause muscle and joint pain, especially if the infection has affected the patient's immune system.
- Cough: In some cases, fascioliasis can cause cough and other respiratory symptoms if the infection has affected the lungs.
It is important to keep in mind that many patients with fascioliasis may be asymptomatic, especially in the early stages of infection. And this is when they are unknowingly carriers, and if they are not properly bathed, it becomes a big problem.

Fortunately, treatment is not complicated, involving the use of antiparasitic drugs to kill the parasite and treat the infection. As well as treating the symptoms.
In general, unless it complicates the liver, the parasite is usually completely eradicated from the body. However, there may also be sequelae, especially if the liver or biliary tract has been severely affected.
This is all for now, obviously, the most important thing in this disease, as in most of them, is to avoid them, and it is basic in this case, it requires good food hygiene.
I hope this post has been educational, if you have anything to add or ask, you can leave it in the comments and so we all benefit.