The exact causes of varicella-zoster virus reactivation are not fully known, but a weakened immune system is believed to be an important factor. As we age, our immune system may become less effective, which increases the risk of developing shingles. It has also been noted that stress, chronic illness and certain medical treatments, such as chemotherapy, can trigger an episode of shingles.
 Source
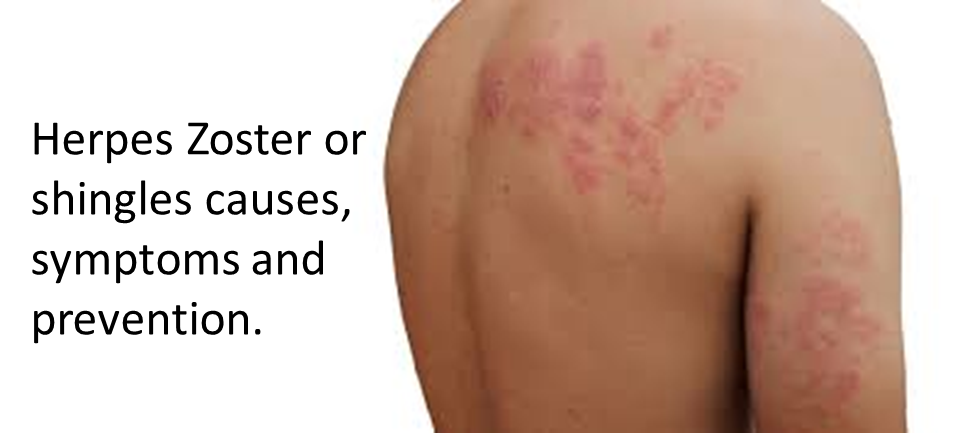
SourceOne of the most characteristic symptoms of shingles is the appearance of a painful, band-like or patchy rash on one side of the body. The rash is usually accompanied by itching, tingling or tenderness in the affected area. Over time, blisters form and fill with fluid, which can cause additional discomfort. In addition to the rash, many people also experience symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue and a general feeling of malaise.
Prevention of shingles is critical to reduce the risk of shingles and its complications. The shingles vaccine is available and is especially recommended for people over the age of 50. The vaccine can help prevent shingles or, if it does develop, reduce the severity of symptoms. It is important to consult a physician to determine if the vaccine is appropriate in each individual case.
In addition to the vaccine, there are steps that can be taken to strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of shingles. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise and sufficient rest, can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of viral infections. Reducing stress is also important, as chronic stress can weaken the immune system. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can be helpful.
In the event of developing shingles, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Early treatment can help reduce the duration and severity of the disease, as well as prevent long-term complications, such as chronic pain known as postherpetic neuralgia.
