English version

Una aventura al planeta rojo: Sondas enviadas a Marte
¡Hola, hola, Hivernautas! Acá estamos en una nueva serie de Astronomía, donde nos adentraremos en el planeta rojo, Marte.
Para la década de 1960, se han hecho múltiples misiones a Marte. Tanto agencias espaciales estatales como empresas privadas han iniciado esta travesía. Es por ello que mediante este post mostraremos inicio las misiones más sobresalientes.
La humanidad ha realizado por el momento más de 50 misiones enviadas a Marte, dichas misiones en su mayoría fueron realizadas por Estados Unidos y Rusia. También hay países con intención de conquistar el espacio y es así como la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), India y China se unieron también a esta carrera.
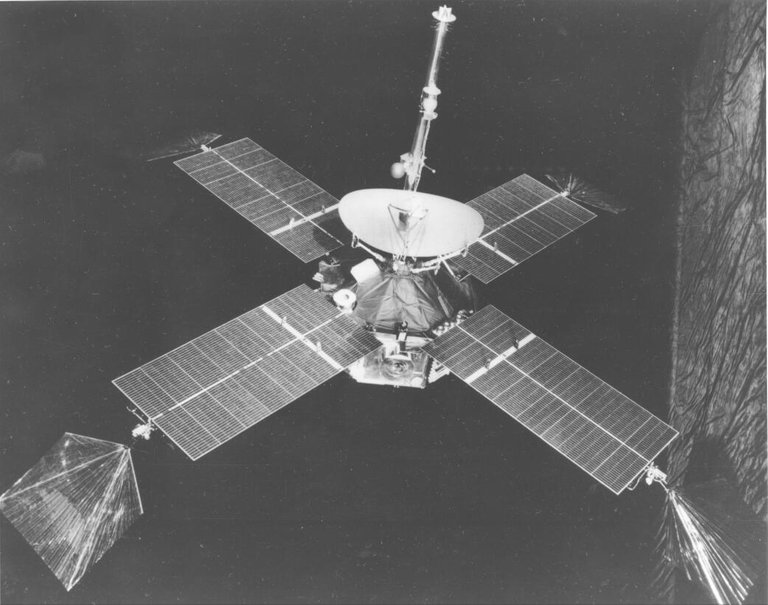
Mariner 4 (1964). Créditos: NASA
La primera misión enviada a Marte la realizó la extinta URSS, la cual no logró el objetivo final debido a una falla en una de las etapas del cohete Molniya 8K78 que ocurrió cuando intentó alcanzar la órbita.
Sin embargo, la Unión Soviética fueron quienes lograron por primera vez, el 2 de diciembre de 1971, llegar a la superficie de Marte con la sonda soviética Mars 3. Al llegar y pasados los 15 minutos, la comunicación se cortó y las imágenes enviadas a la Tierra eran grises con escasos detalles.

Sonda Mars 3 con la parte del módulo de aterrizaje. Créditos: colección del Museo Powerhouse
Por su parte, El correspondiente programa de la NASA dio inicio en 1960 con la misión Mariner 4. Fue la primera en enviar imágenes cercanas de Marte, puesto que logró estar y mantenerse en órbita en 1965. La NASA ha realizado diversas misiones exitosas a Marte, entre ellas Viking 1 y 2 en 1976, Mars Pathfinder en 1996, Spirit y Opportunity en 2003, el Mars Science Laboratory, que incluyó el rover Curiosity, en 2011 y, más recientemente, la misión Mars 2020, que incluye al rover Perseverance.

La Mariner 4 en preparativos para el lanzamiento. Créditos: NASA/JPL.
La Misión Mars Global Surveyor de la NASA fue Lanzada en 1996. Fue la primera nave espacial en orbitar Marte en más de 20 años. La sonda tardó casi dos años en entrar y mantener estabilidad en la órbita del planeta rojo. La misión realizó un estudio de la atmosfera y superficie en su totalidad. La cámara principal generó imágenes, con lo que se realizó un mapeo del planeta y se recopilaron datos sobre su atmósfera y superficie.
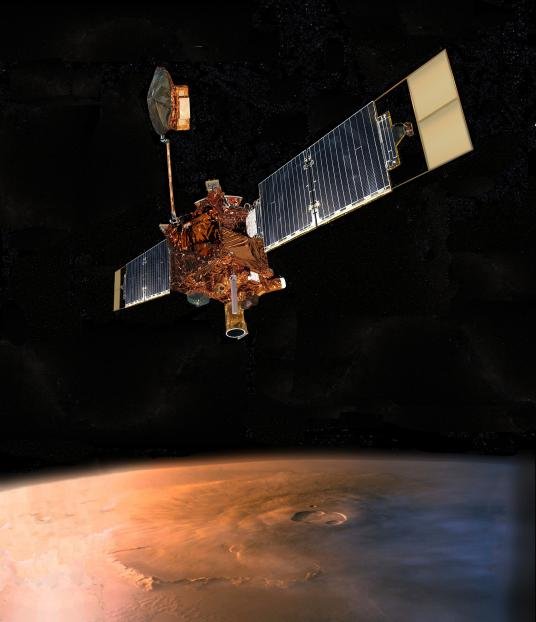

Concepto de la NASA's Mars Global Surveyor (MGS). Créditos: NASA/JPL-Caltech
La misión Mars Express de la ESA, de la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), se lanzó en 2003. Esta se compone de dos partes: un orbitador y un módulo de aterrizaje llamado Beagle 2, el cual falló intentando aterrizar en la superficie de Marte. No obstante, el orbitador ha estado desde entonces realizando estudios importantes en el planeta rojo.

Mars Express. Créditos: Agencia espacial Europea (ESA) 2001
A su vez, la misión Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter de la NASA fue lanzada en el año 2005. La misión también conocida por sus siglas MRO está constituida por una serie de instrumentos científicos diseñados para estudiar el clima, la geología, la atmósfera y el agua en Marte.
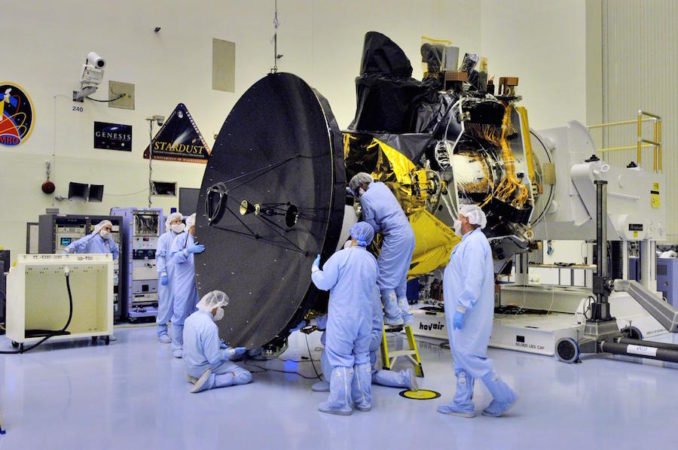

El Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter de la NASA. Imágenes antes de su lanzamiento en 2005. Créditos: NASA
La misión Tianwen-1 de julio de 2020 fue la primera que lanzó la potencia China. La misión incluye un orbitador, un módulo de aterrizaje y un rover. Tianwen-1 es la primera en la historia que combina en un mismo viaje la entrada en órbita de una sonda y el descenso a la superficie de un rover. Los científicos chinos pretenden obtener pruebas más fidedignas de la existencia de agua o hielo en ese planeta, como también realizar investigaciones sobre la composición material de la superficie de Marte.

Tianwen-1 de China. Créditos: Nubalo Studios S.L.
Finalmente, está la misión Mars 2020, que fue lanzada el 30 julio del 2020 y completó un aterrizaje exitoso el 18 de febrero del 2021. Esta incluye el rover Perseverance, un vehículo terrestre de última tecnología y el helicóptero Ingenuity, el cual sirve de guía para encontrar mejores rutas para el Rover. La misión tiene como objetivo buscar signos de vida pasada y recolectar muestras de rocas y suelo para su eventual retorno a la Tierra.

Perseverance / Mars 2020. Créditos: NASA/ESA/CSA/others.
Es así como inicia la carrera para la conquista del planeta rojo. Para la próxima entrega examinaremos más detalles resaltantes de estas expediciones y otros proyectos. Los espero, Hivernautas.
Créditos:
Imagen 1: Autoría propia. Realizada con base en imágenes libres.
Imagen 2: Fuente
Imagen 3: Fuente
Imagen 4: Fuente
Imagen 5: Fuente
Imagen 6: Fuente
Imagen 7: Fuente
Imagen 8: Fuente
Fuentes de consulta:
- https://www.adn40.mx/ciencia/marte-misiones-sondas-mva-especial
- https://mars.nasa.gov/mars-exploration/missions/mars-global-surveyor/
- https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Mars_Express
- https://www.dw.com/es/misi%C3%B3n-china-tianwen-1-env%C3%ADa-nuevas-im%C3%A1genes-desde-marte/a-60310305#:~:text=La%20Tianwen-1%20es%20la%20primera%20misi%C3%B3n%20china%20de,%C3%B3rbita%20y%20el%20descenso%20en%20una%20sola%20misi%C3%B3n.
- https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/
English version

An Adventure to the Red Planet: Probes Sent to Mars
Hello, hello, Hivernauts! Here we are in a new Astronomy series, where we will take a closer look at the red planet, Mars.
By the 1960s, multiple missions to Mars had been made. Both state space agencies and private companies have started this journey. That is why through this post we will show the most outstanding missions.
Humanity has so far carried out more than 50 missions sent to Mars. These missions were mostly carried out by the United States and Russia. There are also countries with the intention of conquering space and this is how the European Space Agency (ESA), India and China also joined this race.

Mariner 4 (1964). Credits: NASA
The first mission sent to Mars was carried out by the extinct USSR, which did not achieve the final objective due to a failure in one of the stages of the Molniya 8K78 rocket that occurred when it tried to reach orbit.
However, the Soviet Union was the one who managed for the first time, on December 2, 1971, to reach the surface of Mars with the Soviet probe Mars 3. Upon arrival and after 15 minutes, communication was cut off and the images sent to Earth were gray with sparse detail.

Mars 3 probe with part of the lander. Credits: Powerhouse Museum Collection
For its part, the corresponding NASA program began in 1960 with the Mariner 4 mission. It was the first to send close-up images of Mars, since it managed to be and remain in orbit in 1965. NASA has carried out several successful missions to Mars, including Viking 1 and 2 in 1976, Mars Pathfinder in 1996, Spirit and Opportunity in 2003, the Mars Science Laboratory, including the Curiosity rover, in 2011, and most recently the Mars 2020 mission, including the Perseverance rover.

Mariner 4 in preparation for launch. Credits: NASA/JPL.
NASA's Mars Global Surveyor Mission was launched in 1996. It was the first spacecraft to orbit Mars in more than 20 years. The probe took almost two years to enter and maintain stability in the orbit of the red planet. The mission conducted a survey of the entire atmosphere and surface. The main camera generated images, thereby mapping the planet and collecting data on its atmosphere and surface.

Concept of NASA's Mars Global Surveyor (MGS). Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
ESA's Mars Express mission, of the European Space Agency (ESA), was launched in 2003. It consists of two parts: an orbiter and a lander called Beagle 2, which failed trying to land on the surface of Mars. However, the orbiter has been conducting important studies on the red planet ever since.

Mars Express. Credits: European Space Agency (ESA) 2001
In turn, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter mission was launched in 2005. The mission, also known by its acronym MRO, is made up of a series of scientific instruments designed to study the climate, geology, atmosphere, and water in Mars.

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Images before its launch in 2005. Credits: NASA
The Tianwen-1 mission in July 2020 was the first to be launched by Chinese powerhouse. The mission includes an orbiter, a lander and a rover. Tianwen-1 is the first in history to combine the entry into orbit of a probe and the descent to the surface of a rover in the same trip. Chinese scientists intend to obtain more reliable evidence of the existence of water or ice on that planet, as well as conduct research on the material composition of the surface of Mars.

China's Tianwen-1. Credits: Nubalo Studios S.L.
Finally, there is the Mars 2020 mission, which was launched on July 30, 2020 and completed a successful landing on February 18, 2021. This includes the Perseverance rover, a state-of-the-art ground vehicle, and the Ingenuity helicopter, which serves as a guide to find better routes for the Rover. The mission aims to search for signs of past life and collect rock and soil samples for eventual return to Earth.

Perseverance / Mars 2020. Credits: NASA/ESA/CSA/others.
This is how the race to conquer the red planet begins. For the next installment we will examine more interesting details of these expeditions and other projects. I wait for you, Hivernauts.
Credits:
Image 1: Autoría propia. Realizada con base en imágenes libres.
Image 2: Fuente
Image 3: Fuente
Image 4: Fuente
Image 5: Fuente
Image 6: Fuente
Image 7: Fuente
Image 8: Fuente
Reference sources:
- https://www.adn40.mx/ciencia/marte-misiones-sondas-mva-especial
- https://mars.nasa.gov/mars-exploration/missions/mars-global-surveyor/
- https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Mars_Express
- https://www.dw.com/es/misi%C3%B3n-china-tianwen-1-env%C3%ADa-nuevas-im%C3%A1genes-desde-marte/a-60310305#:~:text=La%20Tianwen-1%20es%20la%20primera%20misi%C3%B3n%20china%20de,%C3%B3rbita%20y%20el%20descenso%20en%20una%20sola%20misi%C3%B3n.
- https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/




