I greet you all lovely members of this community. A lot has happened this period I have been away on the platform, I sincerely apologize for this expensive disappearance and for starving our knowledge bank for this length of time, it wasn't intentional, it was just a little bit beyond my control and I know I will be forgiven for this 😊.
I must confess that I have really
missed this awesome community and everything happening here I'm currently away from work, and that is why today I bring to us a continuation of the topic I commenced on the world heart day and this second part I tagged the part B. The previous post which was the part A was sort of an intro to today's post which was just meant to sensitize us on the world heart day celebration.
In this current article, I will try my utmost best to make it simple and easy to comprehend as well as explain more about the organ I'm referring to as the power house, routine investigations carried out to check it's activity and state, common heart conditions and preventions of heart conditions, so I will also appreciate if you can go through the part A of this post in my previous post, it will help you understand this current one more.
So I encourage you to follow this writeup with maximum attention so that you will get the message as they say knowledge is key to life.
THE HEART (CONTINUED)
In my previous post the power house being referred to was the heart and I know some persons will be wondering why the comparison. Simply put the heart being the power house of the body means that it's the heart that sustains or supplies the power(blood)required by the body for it to stay alive and function maximally.
So from my explanation above, the heart is responsible for pumping of blood and as we all know blood signifies life so for the body to be alive, there must be blood circulating through out the body and supplying all the organs of our body which is why these organs eg kidney, brain, liver etc also function well.
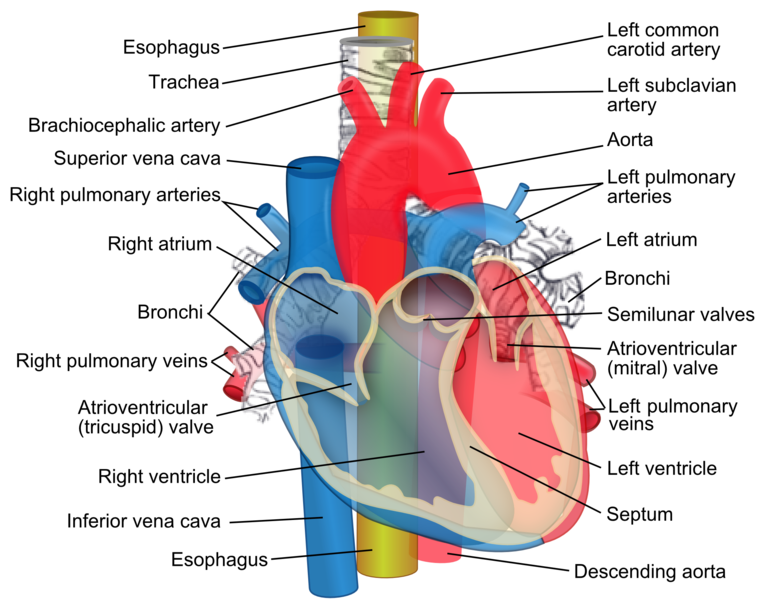
Like I stated earlier, the heart as an organ is divided into three layers and four Chambers and you can see these in my last post for more understanding. To make it easy,I will briefly explain some important structures relating to the heart which will be relevant to this post and they include:
LAYERS:
The heart is divided into three layers which consists of the pericardium,the endocardium and the myocardium.
THE PERICARDIUM
This is the outermost covering of the heart,which has a protective function to both the heart and it's vessels. For this pericardium to be able to guard the heart successfully, it has a particular unique feature. It is a sac that contains fluid which is called pericardial fluid, which helps in protecting the heart from shock due to any form of trauma through a cushioning effect.
So simply put just as you the amniotic sac which contains fluid(amniotic fluid) protects the baby in utero due to its cushioning effect,so also does the pericardium 😊.
THE MYOCARDIUM
This is the second layer of the heart after the pericardium and it is surrounded by the pericardial fluid. From the name myo meaning muscles and cardium meaning heart, the myocardium simply put is the muscular layer of the heart, and this layer is the thickest and really vital when it comes to circulation and availability of blood.
This muscular layer of the heart, is important in the pumping of blood by the heart, and that's why any thing that happens to the muscle will affect the amount of blood pumped out and going into circulation. This is because the heart muscles contracts and relaxes inorder to pump out blood into circulation.
THE ENDOCARDIUM
From the the word Endo means within, while cardium means the heart,this tissue lines the innermost layer of the heart, the valves, the chambers etc.
So these are the three layers of the heart.
CHAMBERS
The heart has four Chambers like I already stated in my previous post and these four parts includes: The right and left atrium, the right and left ventricle. I will encourage that you to visit my previous post to get more information about the heart Chambers.
BLOOD VESSELS
Some of the blood vessels of the heart I will be mentioning in this my post includes: The coronary vessels, the inferior vena cava, superior vena cava, aorta, pulmonary vein and pulmonary artery.
THE CORONARY VESSELS
The word coronary has its origin from corona which is not an english word but latin and we all know what a crown signifies but in this context, the word is used to describe how the blood vessels of the heart unite to form network of vessels encircling and protecting the heart, supplying it with oxygenated blood, as well as carrying away deoxygenated blood from the Heart back to the right atrium.
THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA
From the name, inferior which means from below, simply means that this great vessel of the heart collects all the deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body which are below the diaphragm (systemic circulation), back into the right atrium.
THE SUPERIOR VENA CAVA
From the name, collects all the deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body which is above the diaphragm back into the right atrium.
THE AORTA
This is a large blood vessel that is curved at the upper part, and is in the heart, carries blood pumped out by the left ventricle which is rich in oxygen and nutrients (oxygenated blood), into systemic circulation (the body).
THE PULMONARY VEIN
This is the only vein in the body that carries oxygen rich blood (oxygenated blood), every other vein carries deoxygenated blood. It carries oxygenated blood into the left atrium which delivers it to the left ventricle that pumps it out into circulation.
PULMONARY ARTERY
This is the only artery in the body that carries deoxygenated blood, unlike the others in the body that carries oxygen rich blood. This vessel carries the deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary circulation, where the blood will be enriched with oxygen (oxygenation) before it goes to the left part of the heart.
THE BLOOD
The human blood has different components that makes it up and they include the liquid component and the cellular component. The following make up the blood: The plasma which is the liquid component of the blood and makes up 55% of the total blood volume, while the cellular component (Red blood cells, white blood cell and platelets) makes up 45% of the total blood volume.
The red blood cells on their part contains haemoglobin which helps in the transportation of oxygen in the blood, the white blood cells are known to play a major role in our body's defence ie to protect the body from infections, while the platelets are responsible for blood clotting when ever there is injury inorder to reduce excessive bleeding and blood loss.
In addition,the plasma content of the human blood is seen to contain a greater percentage of water and the nutrients, wastes etc.
It is this blood, that the heart pumps out to circulation that sustains itself and other parts of the body due to the nutrients contained in it.
INTERNAL STRUCTURES
The chambers of the heart are also part of the internal structures, with the valves inclusive and we have four valves in the heart which are:
• The mitral valve (that connects the left ventricle and the left atrium).
• The Tricuspid valve (that connects the right ventricle to the right atrium).
• The pulmonary valve (that connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery).
• The Aortic valve(that connects the left ventricle to the aorta).
NODES
The heart has two nodes, and this nodes are responsible for all the electrical activities in the heart which makes it possible for the heart to be able to perform it's role in the pumping of blood. And this nodes includes:
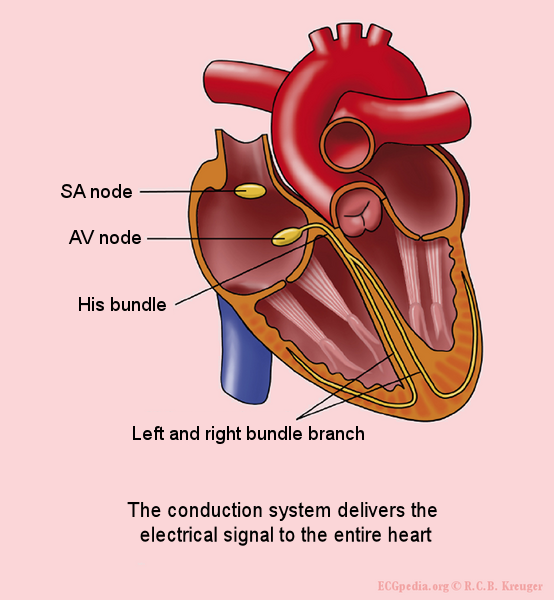
Conducting system of the heart showing the nodes
• SINOATRIAL NODE (SA node)
This is the major node in the heart, and it is located at the right atrium, with the responsibility of generating electrical impulses there in the right atrium which sets the necessary pace for the heart to carry out activities and functions, and that is why this SA node is also called the pacemaker.
This node plays vital role in the heart functioning, because if anything goes wrong with this node, the activities of the heart will be affected negatively. Because of this, pacemaker(artificial SA nodes) implantation is usually carried out surgically on anyone whose SA nodes begins to malfunction, so that this artificial pacemakers will help in generating the electrical impulses necessary for the heart.
• ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE (AV nodes)
The AV node is the second node in the heart, and it's responsibility is to ensure that the electrical impulses generated by the SA node at the right atrium, is carried or transmitted from the atrium to the other parts of the heart, so I will say that this AV node is a transmitter because of its role in moving this electrical impulses.
DISEASES OF THE HEART/PREVENTION
The heart which is an important organ in the body, whose functions and activities affects other organs ,systems and other parts of the body, also can be affected by disease conditions which will alter it's function. And there are so many disease conditions that affects this organ and some of the conditions I will be mentioning here even though I may not go into explain it. Some of the diseases are:
• HEART FAILURE
This is a condition in which the heart is unable to perform It's pumping function and this could be from other disease conditions. And I already stated that it's the role of the myocardium to ensure the heart pumps adequately, so anything that damages the heart muscles, will also affect the pumping.
• MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (HEART ATTACK)
This condition can occur when the heart circulation by the coronary artery is narrowed to the point of occlusion, the muscles of the area of the heart which do not get this oxygen and blood supply, experience death which have it's characteristic symptoms of pains at different parts of the body like the chest,neck etc.
• CORONARY HEART DISEASE
This condition occurs due to the coronary artery being narrowed by fat deposits and because of this, the volume of blood that gets to the heart is reduced, and so the heart having less Oxygen and blood becomes weak and unable to pump effectively.
• CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA
This is a condition in which heart rhythm becomes so irregular either too rapid (tachycardia) or too slow (bradycardia). This irregularity is due to the electrical impulses which may have been altered and because of this, the heart activities becomes affected and may not be able to deliver the required amount of blood.
• VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
This particular condition affects the valves of the heart. Here the valves which have the role of regulating the volume of blood moving from one chamber to the other, may develop issues with it's opening and closing which will affect the movement of blood and can result to even other heart conditions.
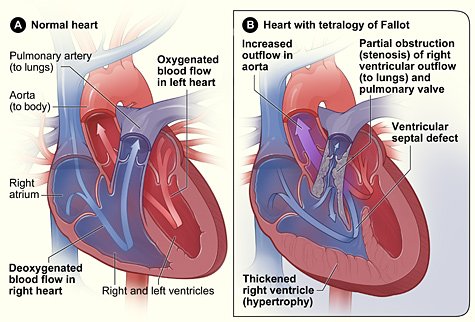
• CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES
These are diseases that affects their the baby(fetus) in the uterus. This conditions happens due to malformations in the heart,or incomplete formation of the heart when the baby is still forming in the womb. TETRALOGY OF FALLOT is an example of some of the congenital disease, the picture below explains the conditions that makes up the tetralogy.
PREVENTION
This heart conditions can actually be prevented from occurring through:
• Regular exercising
• Proper dieting
• Regular cardiovascular check ups
• Regular rest.
INVESTIGATIONS
Some of the examination or investigations that will help in identifying these heart conditions includes:
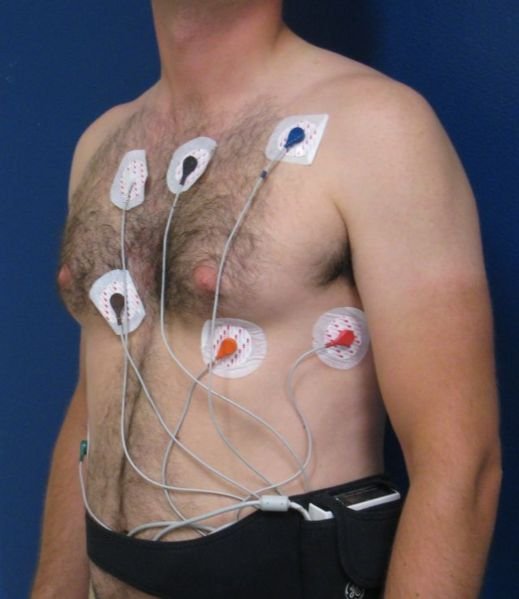
• Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Checks the waves of the heart, to identify if there is any electrical deviations in the heart.
• Echocardiogram (Echo)
Used to check heart sounds to identify when it's abnormal, which will help in making some diagnosis.
Also this investigation helps in diagnosing valvular heart diseases because through the echo, the valves of the heart and blood flow can be examined well.
• Holter ECG
This kind of ECG is done for 24hours in which the device is worn on the individual. It's done inorder to detect any abnormalities in the heart activities which the normal ECG at rest can not be able to detect.
• Stress ECG
This kind of ECG is done when the person is exercising,like jogging , cycling etc to know the state of the heart when it has passed through hectic task or stress and to also help make diagnosis depending on the symptoms an individual presents.
• Blood pressure checks
Helps in identifying when the blood
Is going out of normal, because hypertension is also risky.
• Ambulatory blood pressure checks
This is done for a period of 24hours, in which the device is worn on the individual and the person will go about their routine daily activities with the device on inorder to know how your activities affects the blood pressure of the individual.
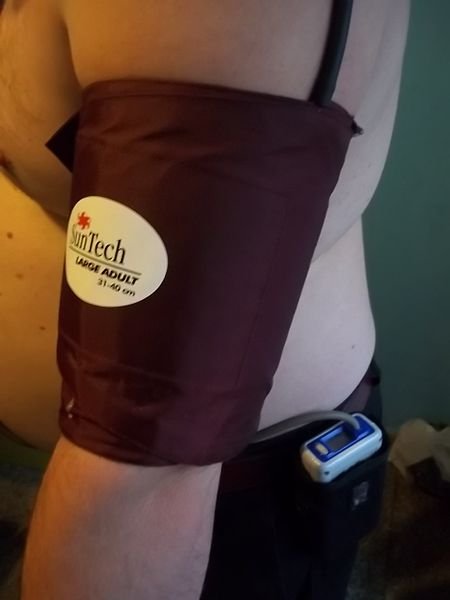
Patient on ambulatory blood pressure device
• Tropinins test
This is a serological (blood) test to check for Tropinins to know if the individual is having myocardial infarction (MI) or not, which will guide the line of diagnosis and treatment. Because Tropinins are proteins that are located in the muscles of the heart and so when it's abnormally high, it shows that heart attack has occurred.
• CT SCAN, MRI,CHEST X-RAYS
They all help in detecting any structural abnormalities in the heart as a confirmation for diagnosis.
The earlier the investigations are done the better, to save the situation early enough.
So I will be drawing the curtain at this point, thanks a lot for your time and patience. See you in my next post.
REFERENCES