Let's assume that you've given birth, and you're postpartum. Remember, that postpartum is considered 1.5 months status post delivery.
What are your burning questions as a new or new again mother?
Let's see... Breastfeeding, Infections, Conceiving Again, and How to Keep Your Newborn ALIVE. That last one is the big one, but let's start with Breastfeeding.
What the Heck is Colostrum and Breast Milk?
After giving birth, the first 2 days of breastfeeding, you're not actually producing breast milk. In fact, you're producing a thick yellow substance called, "colostrum". Colostrum contains antibodies, in which the mother passes on her immunity to the newborn.

It isn't until day 3 or 4, that real breast milk is produced. Breast milk contains water, carbohydrates, fat, protein, and antibodies. Typically, a baby's only source of food for the first 6 months is from breastmilk, which is why many mothers worry about whatever other medications they put in their body, and whether it'll pass through their milk and affect their baby. Important to note that solely breast milk is given, nothing else, not even H20.
Vitamin D
- We get the majority of our Vitamin D from the sun, and most of us are deficient at it. For infants, they barely get any Vitamin D, so they have to fortified formula or supplementation drops starting from the first few days of life. Vitamin D will convert to Calcium, thus supporting bone strength and health.
- If the infant is on formula, they should be given iron-fortified and Vitamin-D fortified formula.
Breastfeeding Technique
- Breastfeed within the first hour of birth.
- If breastfeeding is noisy, double check technique for proper latching. Should hear swallowing, not clicking noises.
- Remember that infants nurse 8-12 times every 24 hours, which equates to feeding every 2 hours.
Sore Nipples
- May be due to too much milk production or backed up, so mother should continue breastfeeding to avoid engorgement
- Monitor for fissures and infection
- Nurse on the least painful breast first
- Apply lanolin or even breast milk to the nipple to protect skin breakdown
- Do not use plastic nipple shields
Maternal and Fetal Benefits
- Reduces uterine involution time
- Maternal-Infant bonding
- Speeds up weight loss
- Reduces risk of breast and ovarian cancer
- Lowers risk of infections, such as necrotizing enterocolitis and acute otitis media
- Reduces risk of asthma and allergies
- Reduces risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Mastitis
- Typically seen in the first 2 months of breastfeeding
- Prevented by proper breastfeeding technique, as engorgement increases risk
- Presents as sudden onset of red, firm, and tender induration on ONE breast
- May require antibiotics, such as dicloxacillin and cephalexin, and bactrim
- ultrasound for breast abscess present
Postpartum Contraception
- Mothers who breastfeed, not having her period, and less than 6 months after delivery tend to ovulate less than a mother who does not breastfeed exclusively.
- Mothers who do not breastfeed resume ovulation around 40 days after giving birth
- Any contraceptives containing estrogen is contraindicated, as it is detrimental for pregnancy
- Postpartum women can switch to progesterone-only contraceptives or an alternative i.e. copper IUD, levonorgestrel, nexplanon, depo-provera, progestin-only pills, or barrier methods.
- Note that norethindrone (Micornor) contains 28 active tablets taken daily, meaning there are no placebos.

You're a Mom Now, so How Do I Keep My Baby ALIVE?
Essentially, you'll want to make sure that the baby is: (1) not lethargic or difficult to arouse, (2) making urine/wet diapers, (3) having bowel movements, and (4) has an appetite and gaining weight each week.
However, here are other things to look out for or to expect if there's an existing condition:
Failure to Thrive
- Weight for age that falls below 3-5% on the growth chart
- In the U.S., we use the World Health Organization growth chart until age 2 years, then switch to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention growth charts
Down Syndrome
- Genetic defect caused by trisomy 21 or chromosome 21, which makes 3 copies of itself instead of 2
- Gives the child an appearance of round, flat face, with upward slanting eyes, and low set ears. The child will have an open mouth chronically due to an enlarged tongue, and present with a short neck.
- Parents will have to be careful about contact sports and avoid trauma, such as using a trampoline.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
- Presents with a small head, narrow eyes, a flat nasal bridge, thin upper lip, and underdeveloped ears.
- Child can have mental retardation or mild developmental defects.
Cryptorchidism
- Empty scrotal sacs, typically due to undescended testicles
- Provider will try to massage the inguinal canal in an attempt to dislodge testicles and have them descend
- Increased risk of testicular cancer if the testicles are not removed from the abdomen - will require surgery
Gonococal Opthalmia Neonatorum
- A congenital gonorrhea infection where symptoms show in 2-5 days after birth... can cause blindness!
- Symptoms include red conjunctiva with purulent discharge and swelling
- Should be cotested for chlamydia and herpes simplex
- Treat with high dose ceftriaxone
- Prophylaxis of erythromycin ointment to eyes immediately after birth
Chlamydia Pneumonia
- Ruled out concomitantly with opthalmia neonatorum
- Presents with frequent cough, bibasilar rales, fast breathing, hyperinflation, and diffused infiltrates on chest xray.
- Treated with erythromycin for 2 weeks
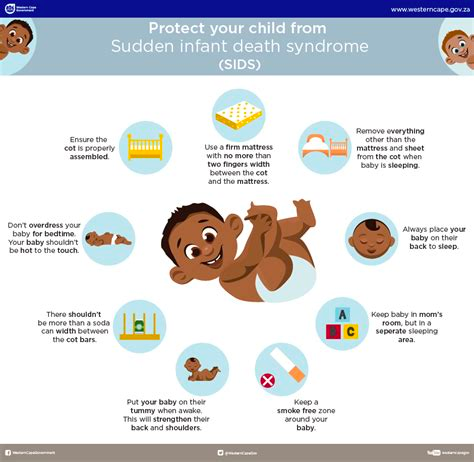
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
- Unexplained, but higher risk with prematurity, low birth weight, maternal smoking and drug use, and poverty
- Reduce risk by positioning infants on their backs ONLY. Also, avoid overheating infant with thick blankets.
Weight loss
- Newborns actually lose weight in the first week of life.
- Formula fed infants lose 5%, and breast fed infants lose 7-10%
- However, weight is regained within 14 days, but if it is not, then assess for dehydration and poor latching
Dehydration
- Defined as a loss of over 10% weight loss
- Symptoms will be lethargy, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, dry mucous membranes, sunken fontanelle, tenting skin turgor, cool skin, blue skin, and low urine output.
- Severe dehydration is an immediate trip to the ER for IV hydration