New to the cryptocurrency and blockchain world?
@onboarder is here to present some fundamental knowledge that will get you up to speed as you navigate through Hive.
Clearly, there are fundamental concepts and practices that cut across many other blockchain projects that are pretty abstract and difficult to understand. Fear not! Since you stumble upon Hive and Leo Finance, I invite you to learn more about the cryptocurrency and blockchain world as you navigate through what Hive offers.
In this series of posts which is called the Onboarder's fundamental knowledge series, I will endeavour to show you some key concepts of cryptocurrency and blockchain concepts through the corresponding elements found on Hive. Take your time to learn!
In this first edition, we look at the concept of Blockchain as immutable records.
Before we proceed, the basic term here to learn is decentralized ledger technology. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain as a continuous long chains of records on a ledger supported by a network of node globally.
Essentially, blockchain is called blockchain because transactions are recorded on it like a virtual ledger, and after it is validated, it gets chained with the previous blocks of transaction records. This continuous chaining right from the genesis block means that all the activities captured as records on the blockchain cannot be changed, making these transaction records immutable. The main reason is that there is a copy of these records somewhere in the world. They continually gets maintained publicly and thus the records are immutable.
For the Hive blockchain, on the https://hiveblockexplorer.com/ site, you can see links to a series of recent blocks. The block number is on the first column.
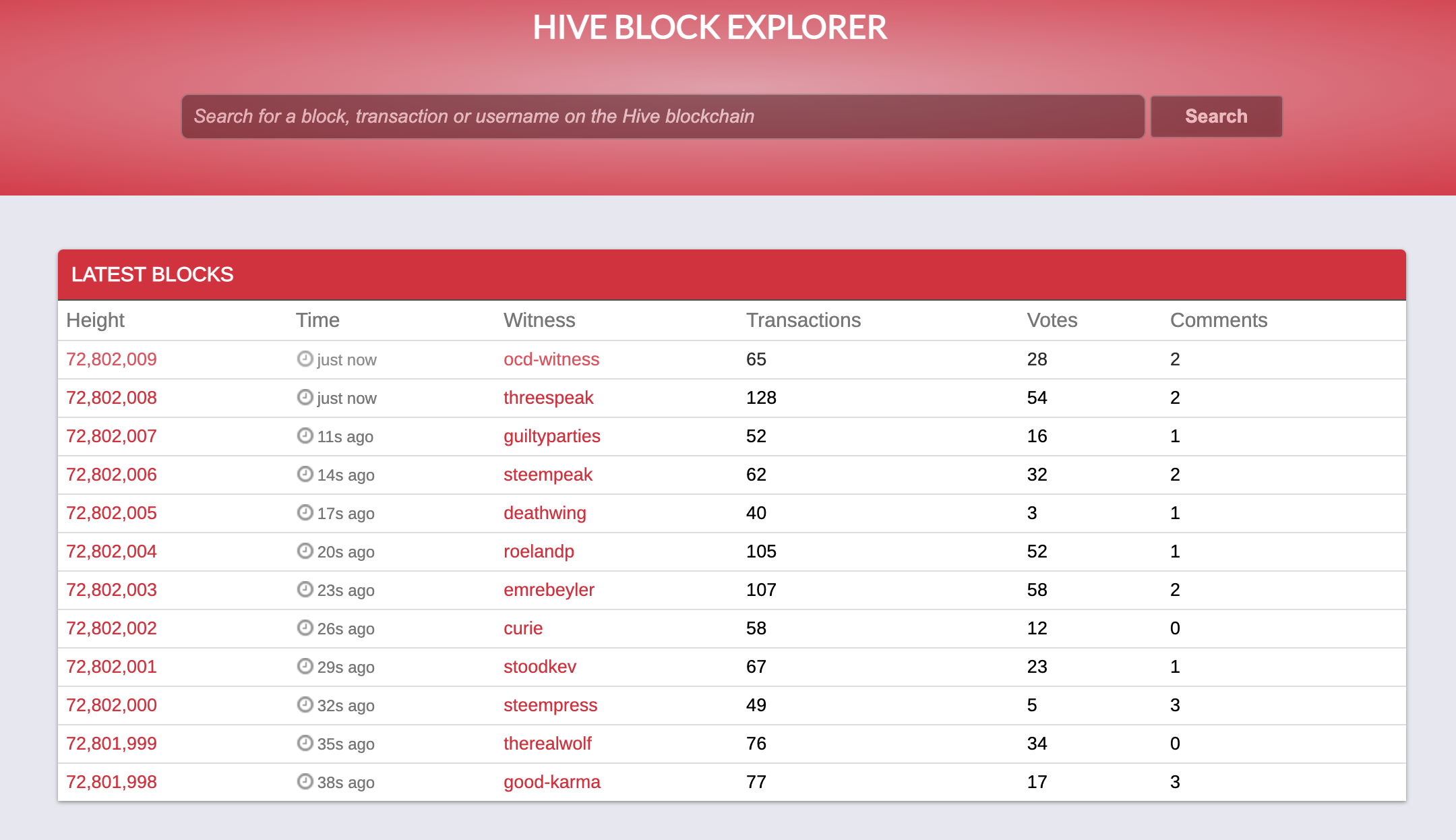
Clicking on the latest block at the point of writing, Block 72,802,009 brings you straight to the record.
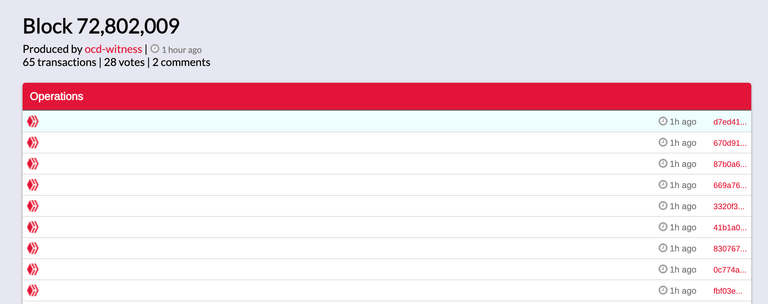
This block has 65 transactions within it.
The screenshot below shows one of the transactions.
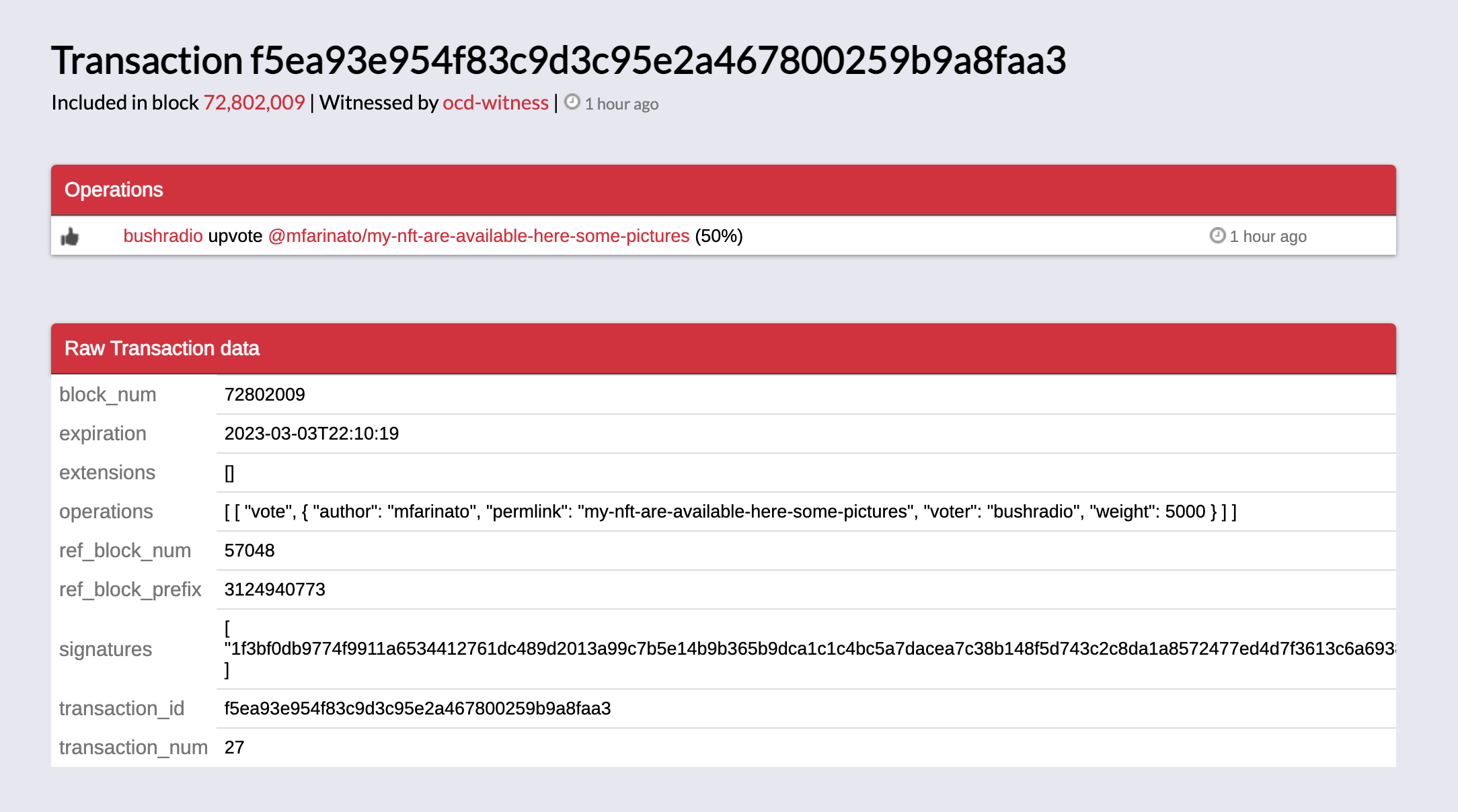
By the time you read these records, you should know that these records had been validated and included in the Hive blockchain as ongoing recording of transactions. Hopefully you also realize that the these records are also public, and thus published and open to scrutiny, and immutable.
This is evidence that blockchain can be viewed as immutable records.
What I have shown is the block explorer of the Hive blockchain, you can also check out the other blockchain explorers.
The same immutability ideals can be found there.
If you have questions about this concept, feel free to ask through the comments below.
Share this with your friends who might be new to Hive. Hopefully, they can get some understanding of such fundamental concepts.
Watch out for the next edition of the Onboarder's fundamental knowledge series!
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta





